Logical schema
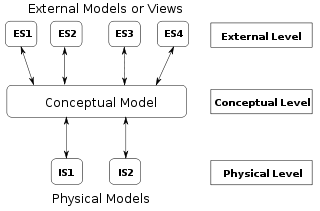
This is as opposed to a conceptual data model, which describes the semantics of an organization without reference to technology.
Logical data models represent the abstract structure of a domain of information.
They are often diagrammatic in nature and are most typically used in business processes that seek to capture things of importance to an organization and how they relate to one another.
For example, a table/column design could be implemented on a collection of computers, located in different parts of the world.
Conceptual, logical and physical data models are very different in their objectives, goals and content.