Cactus alkaloids
In species outside the genus Lophophora, the content and variety of cactus alkaloids are significantly lower, but some contain compounds such as hordenine, N-methyltyramine, mescaline, or pellotine.
[1] A number of psychoactive cacti are found in the genus Echinopsis, such as the San Pedro cactus.
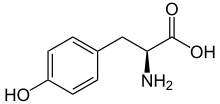
[2]The biosynthesis of cactus alkaloids starts from the amino acid tyrosine and proceeds initially via tyramine and dopamine.
A tetrahydroisoquinoline scaffold can also be constructed from the intermediates of mescaline biosynthesis by a ring closure, resulting in anhalamine and anhalonidine.
Anhalonidine is the biosynthetic precursor of anhalonine, in which a benzodioxole unit is formed from a hydroxyl and a methoxy group.