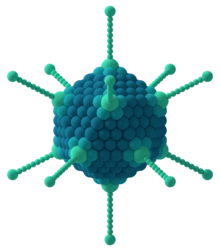
Capsomere
The capsomere is a subunit of the capsid, an outer covering of protein that protects the genetic material of a virus.
Two types of capsomeres constitute the icosahedral capsid: pentagonal (pentons) at the vertices and hexagonal (hexons) at the faces.
In electron micrographs, capsomeres are recognized as regularly spaced rings with a central hole.
The capsomeres protect against physical, chemical, and enzymatic damage and are multiply redundant; having a few protein subunits that are repeated.
This is because the viral genome is being as economic as possible by only needing a few protein codons to make a large structure.