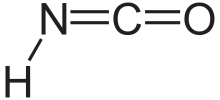Isocyanic acid
[7] Isocyanic acid is the simplest stable chemical compound that contains carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen, the four most commonly found elements in organic chemistry and biology.
Based on these classic assignments, there is no need to invoke a full charged state for the N and O atoms, to explain the vibrational spectral data.
[citation needed][dubious – discuss] The vibrational spectrum is indicative of the presence of a triple bond between the nitrogen and carbon atoms.
[2] Isocyanic acid reacts with amines to give ureas (carbamides): This reaction is called carbamylation.
Low-temperature photolysis of solids containing HNCO creates the tautomer cyanic acid H−O−C≡N, also called hydrogen cyanate.
It was detected using mass spectrometry, and easily dissolves in water, posing a health risk to the lungs.