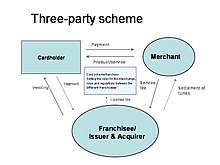
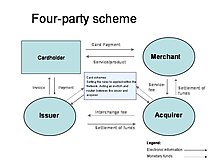
Card scheme
Examples of this setup are Diners Club, Discover Card, and American Express, although in recent times these schemes have also partnered with other issuers and acquirers in order to boost their circulation and acceptance, and Diners Club now operates as a four-party scheme in many regions.
Credit and debit cards work with a four-party scheme, completing an open-circle framework that permits consistent flow of transactions; thus, allowing the banks to handle the whole process.
Card schemes aim to make the transaction convenient and automated for all parties involved in the loop, with the core belief that clients end up spending more than intended when the payment process is simple.
The payment processing company imparts and transfers data for a client's credit or debit card to both the issuing and acquiring bank.
The processor likewise checks for security issues, ensuring that the client's card information is right, and all data is entered correctly.
The process usually takes place at POS terminals in retail locations, or by means of online payment services for websites.
The expenses are paid to the issuing bank and cover costs, such as processing fees, bad debt, and charges due to risk and potential fraudulent activities.