Central European Time
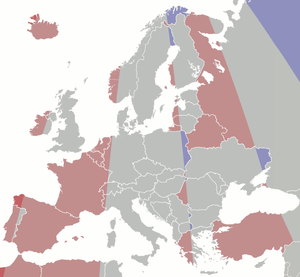
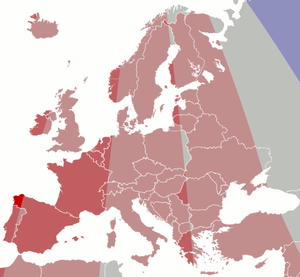
[3] As of 2017,[4] Central European Time is currently used in Albania, Andorra, Austria, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Kosovo (partially recognised as an independent country), Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, San Marino, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain (except the Canary Islands), Sweden, Switzerland and Vatican City.
In 1968[23] there was a three-year experiment called British Standard Time, when the UK and Ireland experimentally employed British Summer Time (GMT+1) all year round; clocks were put forward in March 1968 and not put back until October 1971.
The criteria for drawing time zones is based on many factors including: legal, political, economic, and physical or geographic.
Conversely, there are European areas that have gone for UTC+01:00, even though their "physical" time zone is UTC (typically), UTC−01:00 (westernmost Spain), or UTC+02:00 (e.g. the very easternmost parts of Norway, Sweden, Poland and Serbia).
[26] Historically Gibraltar maintained UTC+01:00 all year until the opening of the land border with Spain in 1982, when it followed its neighbour and introduced CEST.