Finland
[49] In the 16th century, a bishop and Lutheran Reformer Mikael Agricola published the first written works in Finnish;[50] and Finland's current capital city, Helsinki, was founded by King Gustav Vasa in 1555.
[56][55] It is estimated that almost an entire generation of young men was lost during the Great Wrath, due mainly to the destruction of homes and farms, and the burning of Helsinki.
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), led by Vladimir Lenin was the first country to recognise Finland's independence on 4 January 1918.
[78] Finland was also one of the first European countries to strongly promote women's equality, with Miina Sillanpää becoming the first female minister in Finnish history in Väinö Tanner's cabinet in 1926–1927.
[80] The Soviet Union launched the Winter War on 30 November 1939 to annex Finland in accordance with the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact with Nazi Germany to divide Europe into spheres of influence between the two dictatorships.
After two months of negligible progress on the battlefield, as well as heavy losses in men and material,[85] Soviet forces began to advance in February and reached Vyborg (Finnish: Viipuri) in March.
[88] The development of trade with the Western powers, such as the United Kingdom, and the payment of reparations to the Soviet Union led to Finland's transformation from a primarily agrarian society to an industrialised one.
In 1950, 46% of Finnish workers were employed in agriculture and a third lived in urban areas, but new jobs in manufacturing, services and trade quickly attracted people to the cities.
Miscalculated macroeconomic decisions, a banking crisis, the collapse of its largest trading partner, the Soviet Union, and a global economic downturn caused a deep recession in Finland in the early 1990s.
As a result, the old sea bottom turns little by little into dry land: the surface area of the country is expanding by about 7 square kilometres (2.7 sq mi) annually.
The Gulf Stream combines with the moderating effects of the Baltic Sea and numerous inland lakes to explain the unusually warm climate compared with other regions that share the same latitude, such as Alaska, Siberia, and southern Greenland.
Climatic summers (when mean daily temperature remains above 10 °C or 50 °F) in southern Finland last from about late May to mid-September, and in the inland, the warmest days of July can reach over 35 °C (95 °F).
[140] The Finnish Defence Forces consist of a cadre of professional soldiers (mainly officers and technical personnel), currently serving conscripts, and a large reserve.
[157] Amnesty International has expressed concern regarding some issues in Finland, such as the imprisonment of conscientious objectors, and societal discrimination against Romani people and members of other ethnic and linguistic minorities.
Additionally, Finland boasts a well-developed welfare system that encompasses free education and universal healthcare, contributing to its reputation as one of the wealthiest nations.
Finland's soil and climate pose particular challenges for crop production, with harsh winters and relatively short growing seasons, often interrupted by frost.
It has regulated tree cutting, sponsored technical improvements, and established long-term plans to guarantee the sustainability of the country's forests in supplying the wood-processing industries.
[170] As of 2013[update], the 10 largest private sector employers in Finland were Itella, Nokia, OP-Pohjola, ISS, VR, Kesko, UPM-Kymmene, YIT, Metso, and Nordea.
The free and largely privately owned financial and physical Nordic energy markets traded in NASDAQ OMX Commodities Europe and Nord Pool Spot exchanges, have provided competitive prices compared with other EU countries.
However, in recent decades, the Finnish economy has diversified, with companies expanding into fields such as electronics (Nokia), metrology (Vaisala), petroleum (Neste), and video games (Rovio Entertainment), and is no longer dominated by the two sectors of metal and forest industry.
[13][205] Other significant tourist destinations in Lapland also include ski resorts (such as Levi, Ruka and Ylläs)[13][206] and sleigh rides led by either reindeer or huskies.
The 10 largest foreign born groups are (in order) from Estonia, Sweden, Iraq, Russia, China, Ukraine, India, Somalia, Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam and Turkey.
Finnish predominates nationwide while Swedish is spoken in some coastal areas in the west and south (with towns such as Ekenäs,[225] Pargas,[226] Närpes,[226] Kristinestad,[227] Jakobstad[228] and Nykarleby.
The era saw a rise of poets and novelists who wrote in Finnish, notably the national writer of Finland, Aleksis Kivi (The Seven Brothers), and Minna Canth, Eino Leino, and Juhani Aho.
Most famous of them were Frans Eemil Sillanpää, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1939, historical novelist Mika Waltari, and Väinö Linna with his The Unknown Soldier and Under the North Star trilogy.
Finns have made major contributions to handicrafts and industrial design: among the internationally renowned figures are Timo Sarpaneva, Tapio Wirkkala and Ilmari Tapiovaara.
Finnish architecture is famous around the world, and has contributed significantly to several styles internationally, such as Jugendstil (or Art Nouveau), Nordic Classicism and functionalism.
Architect Alvar Aalto is regarded as among the most important 20th-century designers in the world;[289] he helped bring functionalist architecture to Finland, but soon was a pioneer in its development towards an organic style.
Alongside Sibelius, the distinct Finnish style of music was created by Oskar Merikanto, Toivo Kuula, Erkki Melartin, Leevi Madetoja and Uuno Klami.
[303][304] In the film industry, notable modern directors include brothers Mika and Aki Kaurismäki, Dome Karukoski, Antti Jokinen, Jalmari Helander, and Renny Harlin.














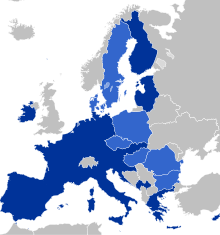
the Eurozone the European Union