Central line (geometry)
In geometry, central lines are certain special straight lines that lie in the plane of a triangle.
The special property that distinguishes a straight line as a central line is manifested via the equation of the line in trilinear coordinates.
This special property is related to the concept of triangle center also.
The concept of a central line was introduced by Clark Kimberling in a paper published in 1994.
[1][2] Let △ABC be a plane triangle and let x : y : z be the trilinear coordinates of an arbitrary point in the plane of triangle △ABC.
A straight line in the plane of △ABC whose equation in trilinear coordinates has the form
is a triangle center, is a central line in the plane of △ABC relative to △ABC.
[2][3][4] The geometric relation between a central line and its associated triangle center can be expressed using the concepts of trilinear polars and isogonal conjugates.
is the trilinear polar of the triangle center X.
is the isogonal conjugate of the triangle center X.
is the trilinear polar of the isogonal conjugate of the triangle center
Let Xn be the nth triangle center in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers.
The central line associated with Xn is denoted by Ln.
The central line associated with the incenter X1 = 1 : 1 : 1 (also denoted by I) is
[6] The trilinear coordinates of the centroid X2 (also denoted by G) of △ABC are:
The trilinear coordinates of the circumcenter X3 (also denoted by O) of △ABC are:
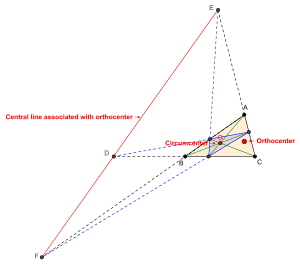
[8] The trilinear coordinates of the orthocenter X4 (also denoted by H) of △ABC are:
The trilinear coordinates of the nine-point center X5 (also denoted by N) of △ABC are:[9]
{\displaystyle \cos(B-C):\cos(C-A):\cos(A-B).}
{\displaystyle x\cos(B-C)+y\cos(C-A)+z\cos(A-B)=0.}
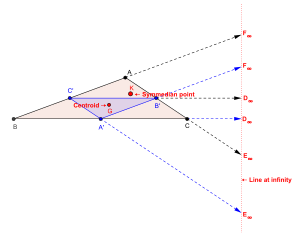
The trilinear coordinates of the symmedian point X6 (also denoted by K) of △ABC are:
The Euler line of △ABC is the line passing through the centroid, the circumcenter, the orthocenter and the nine-point center of △ABC.
The trilinear equation of the Euler line is
This is the central line associated with the triangle center X647.
The Nagel line of △ABC is the line passing through the centroid, the incenter, the Spieker center and the Nagel point of △ABC.
The trilinear equation of the Nagel line is
{\displaystyle xa(b-c)+yb(c-a)+zc(a-b)=0.}
This is the central line associated with the triangle center X649.
The Brocard axis of △ABC is the line through the circumcenter and the symmedian point of △ABC.
This is the central line associated with the triangle center X523.