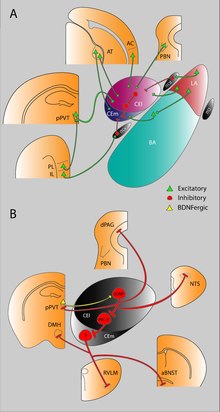
Central nucleus of the amygdala
[1][2] It "serves as the major output nucleus of the amygdala and participates in receiving and processing pain information.
"[3][4][5][6] CeA "connects with brainstem areas that control the expression of innate behaviors and associated physiological responses.
"[7] CeA is responsible for "autonomic components of emotions (e.g., changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration) primarily through output pathways to the lateral hypothalamus and brain stem."
"[8] The regions described as amygdala nuclei encompass several structures with distinct connectional and functional characteristics in humans and other animals.
[12] The ventral amygdalofugal pathway carries output from the central and basolateral nuclei and delivers it to a number of targets; namely, the medial dorsal nucleus of the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the basal forebrain, the brain stem, septal nuclei and nucleus accumbens.