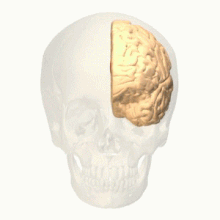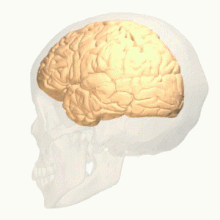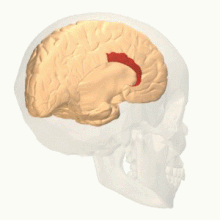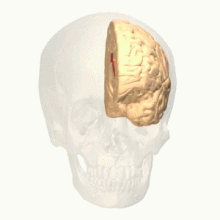
Anterior cingulate cortex
It is involved in certain higher-level functions, such as attention allocation,[1] reward anticipation, decision-making, impulse control (e.g. performance monitoring and error detection),[2] and emotion.
The anterior cingulate cortex can be divided anatomically based on cognitive (dorsal), and emotional (ventral) components.
By contrast, the ventral part of the ACC is connected with the amygdala, nucleus accumbens, hypothalamus, hippocampus, and anterior insula, and is involved in assessing the salience of emotion and motivational information.
[9] A typical task that activates the ACC involves eliciting some form of conflict within the participant that can potentially result in an error.
[11] Conflict occurs because people's reading abilities interfere with their attempt to correctly name the word's ink color.
Many studies attribute specific functions such as error detection, anticipation of tasks, attention,[11][12] motivation, and modulation of emotional responses to the ACC.
Varying levels of dopamine are believed to influence the optimization of this filter system by providing expectations about the outcomes of an event.
[17] Research on the occurrence of the feedback ERN shows evidence that this potential has larger amplitudes when violations of expectancy are large.
[5] Summarizing the evidence found by ERN studies, it appears to be the case that ACC receives information about a stimulus, selects an appropriate response, monitors the action, and adapts behavior if there is a violation of expectancy.
In an interesting expansion of the previously described experiment, the effects of rewards and costs on ACC's activation during error commission was examined.
[21] Participants performed a version of the Eriksen flanker task using a set of letters assigned to each response button instead of arrows.
Taken together, these findings indicate that both the dorsal and rostral areas are involved in evaluating the extent of the error and optimizing subsequent responses.
A study confirming this notion explored the functions of both the dorsal and rostral areas of the ACC involved using a saccade task.
An anti-saccade requires suppression of a distracting cue because the target appears in the opposite location causing the conflict.
Whenever the dorsal area was active, fewer errors were committed providing more evidence that the ACC is involved with effortful performance.
The second finding showed that, during error trials, the ACC activated later than for correct responses, clearly indicating a kind of evaluative function.
Greater ACC activation levels were present in more emotionally aware female participants when shown short 'emotional' video clips.
Crick bases this suggestion on scans of patients with specific lesions that seem to interfere with their sense of independent will, such as alien hand syndrome.
Behavior that is associated with lesions in the ACC includes: inability to detect errors, severe difficulty with resolving stimulus conflict in a Stroop task, emotional instability, inattention, and akinetic mutism.
They used magnetic resonance spectroscopy to assess the balance of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission by measuring glutamate and GABA levels in anterior cingulate cortex and supplementary motor area of healthy volunteers and participants with OCD.
[31] Recent SDM meta-analyses of voxel-based morphometry studies comparing people with OCD and healthy controls has found people with OCD to have increased grey matter volumes in bilateral lenticular nuclei, extending to the caudate nuclei, while decreased grey matter volumes in bilateral dorsal medial frontal/anterior cingulate cortex.
[32][33] These findings contrast with those in people with other anxiety disorders, who evince decreased (rather than increased) grey matter volumes in bilateral lenticular / caudate nuclei, while also decreased grey matter volumes in bilateral dorsal medial frontal / anterior cingulate gyri.
PTSD diagnosis and related symptoms such as skin conductance response (SCR) to "potentially startling sounds" were found to be correlated with reduced ACC volume.