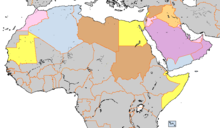
Charter of the Arab League
Concluded in 1945, the agreement aims to strengthen relations and improve cooperation in various areas between signatory Arab countries, while also respecting and preserving their sovereignty.
[citation needed] Since then, governance of the Arab League has been based on the duality of supra-national institutions and the sovereignty of its member states.
[citation needed] Preservation of individual statehood derived its strengths from the natural preference of ruling elites to maintain their power and independence in decision making.
[citation needed] The Charter was concluded on 22 March 1945 by the governments of Syria, Transjordan, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Egypt, and North Yemen.
"[2] The member states of the Arab League represent all forms of government, including monarchies, both absolute and constitutional, as well as republics.