Greece
Philip II of Macedon united most of present-day Greece in the fourth century BC, with his son Alexander the Great rapidly conquering much of the known ancient world from the eastern Mediterranean to northwestern India.
Over the first hundred years, the Kingdom of Greece sought territorial expansion, which was mainly realised in the early 20th century during the Balkan Wars and up until the catastrophic defeat of its Asia Minor Campaign in 1922.
[30][31] Poetry shaped beliefs to the Olympian gods, but ancient Greek religion had no priestly class or systematic dogmas and encompassed other currents, such as popular cults, like that of Dionysus, mysteries and magic.
The Greek victories in the Greco-Persian Wars are a pivotal moment in history,[38] as the 50 years of peace afterwards are known as the Golden Age of Athens, a seminal period that laid many foundations of Western civilisation.
[39] Weakened by constant wars among them during the 4th century BC, the Greek poleis were subjugated to the rising power of the kingdom of Macedon under king Philip II into an alliance known as the Hellenic League.
After fierce conflict amongst themselves, the generals that succeeded Alexander and their successors founded large personal kingdoms in the areas he had conquered, such as that of the Ptolemies in Egypt and of the Seleucids in Syria, Mesopotamia and Iran.
[44] Aspiring to maintain their autonomy and independence from the Antigonid kings of the Macedonians, many poleis of Greece united in koina or sympoliteiai i.e. federations, while after the establishment of economic relations with the East, a stratum of wealthy euergetai dominated their internal life.
[67][full citation needed] Following the Fourth Crusade and fall of Constantinople to the "Latins" in 1204, mainland Greece was split between the Greek Despotate of Epirus and French rule[68] (the Frankokratia).
In the 18th century, Greek merchants came to dominate trade within the Ottoman Empire, established communities throughout the Mediterranean, the Balkans, and Europe,[86] and used their wealth to fund educational activities that brought younger generations into contact with Western ideas.
[93] The Ottoman Sultan Mahmud II negotiated with Mehmet Ali of Egypt, who agreed to send his son Ibrahim Pasha with an army, in return for territorial gain.
Tensions appeared between him and local interests and, following his assassination in 1831 and the London Conference of 1832, Britain, France and Russia installed Bavarian Prince Otto von Wittelsbach as monarch.
[110] The government, aiming to quell Komitadjis and detach the Slavophone peasants of the region from Bulgarian influence, sponsored a guerrilla campaign in Ottoman-ruled Macedonia, known as the Macedonian Struggle, which ended with the Young Turk Revolution in 1908.
The resultant Greek exodus from Asia Minor was made permanent, and expanded, in an official population exchange between Greece and Turkey, as part of the Treaty of Lausanne which ended the war.
[131] King Constantine II's dismissal of George Papandreou's centrist government in 1965 prompted political turbulence, which culminated in a coup in 1967 by the Greek junta, led by Georgios Papadopoulos.
On 20 July 1974, Turkey invaded the island of Cyprus in response to a Greek-backed Cypriot coup, triggering a crisis in Greece that led to the regime's collapse and restoration of democracy through Metapolitefsi.
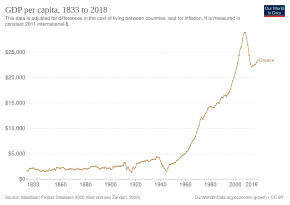
Investments in industrial enterprises and heavy infrastructure, as well as funds from the European Union and growing revenue from tourism, shipping, and a fast-growing service sector raised the standard of living.
[139] Simultaneously, Tsipras, and the leader of North Macedonia, Zoran Zaev, signed the Prespa Agreement, solving the naming dispute that had strained the relations and eased the latter's way to become a member of the EU and NATO.
The country lies approximately between latitudes 34° and 42° N, and longitudes 19° and 30° E, with the extreme points being:[152] the village Ormenio in the North and the islands Gavdos (South), Strongyli near Kastellorizo/Megisti (East), and Othonoi (West).
It consists of 120 articles, provides for a separation of powers into executive, legislative, and judicial branches, and grants extensive specific guarantees (further reinforced in 2001) of civil liberties and social rights.
However, many refugees who settled in former Ottoman Muslim villages in Central Macedonia, and were defined as Christian Orthodox Caucasus Greeks, arrived from the former Russian Transcaucasus province of Kars Oblast, after it had been retroceded to Turkey prior to the population exchange.
[340] Icaria is subsequently classified as a "Blue Zone", a region where people allegedly live longer than average and have lower rates of cancer, heart disease, or other chronic illnesses.
The ancient Greeks pioneered in many fields that rely on systematic thought, including logic, biology, geometry, government, geography, medicine, history,[344] philosophy,[345] physics, and mathematics.
Other modern Greek architects include Anastasios Metaxas, Lysandros Kaftanzoglou, Panagis Kalkos, Ernst Ziller, Xenophon Paionidis, Dimitris Pikionis, and Georges Candilis.
During the late 19th and early 20th century, the Athenian theatre scene was dominated by revues, musical comedies, operettas and nocturnes and notable playwrights included Spyridon Samaras, Dionysios Lavrangas, Theophrastos Sakellaridis.
[366] Rebetiko, initially a music associated with the lower classes, later reached greater acceptance as the rough edges of its overt subcultural character were softened and, sometimes to the point of unrecognisability.
[366] In the 20th century, Greek composers had significant impact on the development of avant garde and modern classical music, with figures such as Iannis Xenakis, Nikos Skalkottas, and Dimitri Mitropoulos achieving international prominence.
Some dishes can be traced back to ancient Greece like skordalia (a thick purée of walnuts, almonds, crushed garlic and olive oil), lentil soup, retsina (white or rosé wine sealed with pine resin) and pasteli (candy bar with sesame seeds baked with honey).
[382] Finos Film contributed in this period with movies such as Λατέρνα, Φτώχεια και Φιλότιμο, Madalena, I theia ap' to Chicago, Το ξύλο βγήκε από τον Παράδεισο and many more.
Yorgos Lanthimos has received four Academy Award nominations for his work, including Best Foreign Language Film for Dogtooth (2009), Best Original Screenplay for The Lobster (2015), and Best Picture and Best Director for The Favourite (2018).
In addition, there are four mandatory official public holidays: 25 March (Greek Independence Day), Easter Monday, 15 August (Assumption or Dormition of the Holy Virgin), and 25 December (Christmas).
















embassy
embassy in another country
general consulate
no representation
Greece