Civil Rights Act
[15] Congressman James F. Wilson summarized what he considered to be the purpose of the act as follows, when he introduced the legislation in the House of Representatives:[16] It provides for the equality of citizens of the United States in the enjoyment of "civil rights and immunities."
In particular, the act discussed the need to provide "reasonable protection to all persons in their constitutional rights of equality before the law, without distinction of race or color, or previous condition of slavery or involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime, whereof the party shall have been duly convicted.
For example, Representative William Lawrence argued that Congress had power to enact the statute because of the Privileges and Immunities Clause in Article IV of the original unamended Constitution, even though courts had suggested otherwise.
In Hodges v. United States (1906) the Court addressed a possible Thirteenth Amendment rationale for the Enforcement Acts, and found that the federal government did not have the authority to punish a group of men for interfering with black workers through whitecapping.
In 1883, the Supreme Court ruled in the Civil Rights Cases that the public accommodation sections of the act were unconstitutional, saying Congress was not afforded control over private persons or corporations under the Equal Protection Clause.
In the late 19th and early 20th century, the legal justification for voiding the Civil Rights Act of 1875 was part of a larger trend by the United States Supreme Court majorities to invalidate most government regulations of the private sector, except when dealing with laws designed to protect traditional public morality.
After the Supreme Court ruled school segregation unconstitutional in 1954 in Brown v. Board of Education, Southern Democrats began a campaign of "massive resistance" against desegregation, and even the few moderate white leaders shifted to openly racist positions.
Despite being the majority in numerous counties and congressional districts in the South, most black people had been effectively disfranchised by discriminatory voter registration rules and laws in those states since the late 19th and early 20th centuries that were heavily instituted and propagated by Southern Democrats.
This specter of military involvement in domestic politics became a worry not just for moderate previous supporters of the bill such as Bourke Hickenlooper (R-IA) - who after Russell's speech referred to Title III as a "violation of the civil rights of the white race.
[81] To prevent a quorum call that could have relieved the filibuster by allowing the Senate to adjourn, cots were brought in from a nearby hotel for the legislators to sleep on while Thurmond discussed increasingly irrelevant and obscure topics.
Initially, Celler had a difficult time acquiring the signatures necessary, with many Representatives who supported the civil rights bill itself remaining cautious about violating normal House procedure with the rare use of a discharge petition.
"[99][100] Strong opposition to the bill also came from Senator Strom Thurmond, who was still a Democrat at the time: "This so-called Civil Rights Proposals [sic], which the President has sent to Capitol Hill for enactment into law, are unconstitutional, unnecessary, unwise and extend beyond the realm of reason.
"[101] After the filibuster had gone on for 54 days, Senators Mansfield, Hubert Humphrey, Everett Dirksen, and Thomas Kuchel introduced a substitute bill that they hoped would overcome it by combining a sufficient number of Republicans as well as core liberal Democrats.
The prohibition on sex discrimination was added to the Civil Rights Act by Howard W. Smith, a powerful Virginia Democrat who chaired the House Rules Committee and strongly opposed the legislation.
For example, Moreton Rolleston, the owner of a motel in Atlanta, Georgia, said he should not be forced to serve black travelers, saying, "the fundamental question [...] is whether or not Congress has the power to take away the liberty of an individual to run his business as he sees fit in the selection and choice of his customers".
[133] Although these acts helped empower courts to remedy violations of federal voting rights, strict legal standards made it difficult for the Department of Justice to successfully pursue litigation.
[145]: 253 President Lyndon B. Johnson recognized this, and shortly after the 1964 elections in which Democrats gained overwhelming majorities in both chambers of Congress, he privately instructed Attorney General Nicholas Katzenbach to draft "the goddamndest, toughest voting rights act that you can".
[145]: 264 On February 18 in Marion, Alabama, state troopers violently broke up a nighttime voting-rights march during which officer James Bonard Fowler shot and killed young African-American protester Jimmie Lee Jackson, who was unarmed and protecting his mother.
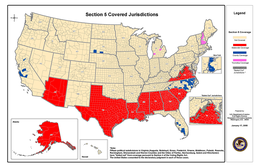
[131] The United States Supreme Court explained this in South Carolina v. Katzenbach (1966) with the following words: In recent years, Congress has repeatedly tried to cope with the problem by facilitating case-by-case litigation against voting discrimination.
Perfecting amendments in the Civil Rights Act of 1960 permitted the joinder of States as parties defendant, gave the Attorney General access to local voting records, and authorized courts to register voters in areas of systematic discrimination.
Even when favorable decisions have finally been obtained, some of the States affected have merely switched to discriminatory devices not covered by the federal decrees, or have enacted difficult new tests designed to prolong the existing disparity between white and Negro registration.
Congress had found that case-by-case litigation was inadequate to combat widespread and persistent discrimination in voting, because of the inordinate amount of time and energy required to overcome the obstructionist tactics invariably encountered in these lawsuits.
In response, Dirksen offered an amendment that exempted from the coverage formula any state that had at least 60 percent of its eligible residents registered to vote or that had a voter turnout that surpassed the national average in the preceding presidential election.
It would have allowed the attorney general to appoint federal registrars after receiving 25 serious complaints of discrimination against a jurisdiction, and it would have imposed a nationwide ban on literacy tests for persons who could prove they attained a sixth-grade education.
The new language was crafted as a compromise designed to eliminate the need for direct evidence of discriminatory intent, which is often difficult to obtain, but without embracing an unqualified "disparate impact" test that would invalidate many legitimate voting procedures.
In particular, the court held that even where the three Gingles preconditions are satisfied, a jurisdiction is unlikely to be liable for vote dilution if its redistricting plan contains a number of majority-minority districts that is proportional to the minority group's population size.
However, the regulations specify that in rental housing, a landlord may not condition widening a bathroom doorway to provide wheelchair access, to its return to its former narrow state upon the end of the tenancy, since it will not interfere with the next tenants use and enjoyment of the premises.
[327] On March 16, 1988, President Ronald Reagan vetoed the bill by arguing that the Act represented an overexpansion of governmental power over private organizational decision-making and "would diminish substantially the freedom and independence of religious institutions in our society.
Title VII, passed in the 1960s when it was assumed that Southern juries could not render a fair verdict, allowed only trial by the court and provided for only traditional equitable remedies: back pay, reinstatement, and injunctions against future acts of discrimination.
In addition, the Court's narrow reading of the phrase "make or enforce contracts" eliminated any liability under Section 1981 for lost promotions and most other personnel decisions that did not constitute a refusal to hire on the basis of race or color.