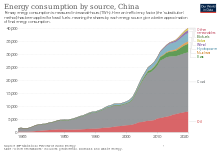
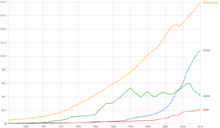
Coal in China
The Chinese central government has continued efforts to curb new coal plant construction while expanding renewable, nuclear, and natural gas power generation.
[1] However, coal consumption remained high, with fossil fuel power generation increasing by 1.5% in 2023 due to surging electricity demand, particularly from energy-intensive sectors like AI, automation, and data centers.
By May 2024, clean energy accounted for 44% of China’s electricity generation, pushing coal’s share to a record low of 53%.
[2] In September 2021, China pledged to end financing for overseas coal power plants,[6] leading to the cancellation of at least 15 projects by April 2022.
[8] Historians suspects that the Chinese were involved in the surface mining of coal around 3490 BC, pioneering the pre-modern world.
Both Chinese and European miners preferred to use drift mines sunk horizontally into the hillside for drainage of water.
[33] That year, Shanxi's major coal producers planned to boost production to address a significant output drop that resulted in a rare 4.1% national decline—the first since 2020.
The China Coal Transportation and Distribution Association predicts continued import growth, driven by rising demand from the steel industry, revitalization efforts in the real estate sector, and favorable import conditions from Mongolia and Russia due to recent export duty waivers.
[citation needed] The consumption of coal is largely in power production, aside from this, there is a lot of industry and manufacturing use along with a comparatively small amount of domestic use in poorer households for heating and cooking.
[43] The think tank Carbon Tracker estimated in 2020 that the average coal fleet loss was about 4 USD/MWh and that about 60% of power stations were cashflow negative in 2018 and 2019.
[53] This was followed up in January 2017 when the NEA canceled a further 103 coal power plants, eliminating 120 GW of future coal-fired capacity, despite the resistance of local authorities mindful of the need to create jobs.
[61]: 70 The NDRC responded by relaxing some environmental standards and the government allowed coal-fired power plants to defer tax payments.
This fills homes with high levels of toxic metals leading to bad indoor air quality (IAQ).
[65] In 2007, the use of coal and biomass (collectively referred to as solid fuels) for domestic purposes was nearly ubiquitous in rural households but declining in urban homes.
Measured pollution levels in homes using solid fuels generally exceeded China's IAQ air quality standards.
Technologies exist to improve indoor air quality, notably the installation of a chimney and modernized bioenergy but need more support to make a larger difference.
[69] It is believed that a continued increase in coal power in China may undermine international initiatives to decrease carbon emissions, such as the Paris Agreement.
"[73] In addition to environmental and health costs at home, China's dependence on coal is cause for concern on a global scale.
Due in large part to the emissions caused by burning coal, China is now the number one producer of carbon dioxide, responsible for a full quarter of the world's CO2 output.
[74] The country has taken steps towards battling climate change by pledging to cut its carbon intensity (the amount of CO2 produced per dollar of economic output) by about 40 percent by 2020, compared to 2005 levels.
[78]: 70 The National Development and Reform Commission responded by relaxing some environmental standards and the government allowed coal-fired power plants to defer tax payments.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), linked to exposure to fine particulates, SO2, and cigarette smoke among other factors, accounted for 26% of all deaths in China in 1988.
[85] A report by the World Bank in cooperation with the Chinese government found that about 750,000 people die prematurely in China each year from air pollution.
The closure of about 1,000 dangerous small mines in 2008 helped to cut in half the average number of miners killed, to about six a day, in the first six months of 2009, according to the government.
[88] In the first nine months of 2009, China's coal mines had eleven major accidents with 303 deaths, with gas explosions the leading cause, according to the central government.
Most accidents are blamed on failures to follow safety rules, including a lack of required ventilation or fire control equipment.
[89] Source: State Administration of Work Safety[92] As of 2018[update] China is exporting technology, for example for coal mining in Turkey.
[94] Coal production employed 2.6 million in 2020 so a just transition is important, but renewable energy creates more jobs per yuan invested.
[95] Since 2004, some local governments in Shanxi have required that coal mining companies set aside funds for investing in noncoal business like agriculture and produce processing.
[100] At the 2021 United Nations General Assembly, Chinese President Xi Jinping announced China's commitment to not building new coal-fired power projects abroad, marking a significant step towards addressing climate change.