Coal power in the United States
Due to measures such as scrubbers air pollution from the plants kills far fewer people nowadays, but deaths in 2020 from PM25 have been estimated at 1600.
[7] Environmentalists say that political action is needed to close them faster, to also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and better limit climate change.
[9] The first AC power station was opened by General Electric in Ehrenfeld, Pennsylvania in 1902, servicing the Webster Coal and Coke Company.
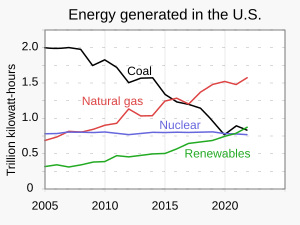
The decline has been linked to the increased availability of natural gas, decreased consumption,[10] renewable power, and more stringent environmental regulations.
The Environmental Protection Agency has advanced restrictions on coal plants to counteract mercury pollution, smog, and global warming.
Utility companies have shut down and retired aging coal-fired power plants following the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) implementation of the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAP).
[25] In Texas, the price drop of natural gas has reduced the capacity factor in 7 of the state's coal plants (max.
[27][28] A 2015 study by a consortium of environmental organizations concluded that US Government subsidies for coal production are around $8/ton for the Powder River Basin.
[32] In the United States, three coal-fired power plants reported the largest toxic air releases in 2001:[33] The Environmental Protection Agency classified the 44 sites as potential hazards to communities, which means the waste sites could cause death and significant property damage if an event such as a storm or a structural failure caused a spill.
The storage facilities hold the noncombustible ingredients of coal and the ash trapped by equipment designed to reduce air pollution.
[40] In 2007, 59 proposed coal plants were canceled, abandoned, or placed on hold by sponsors as a result of financing obstacles, regulatory decisions, judicial rulings, and new global warming legislation.