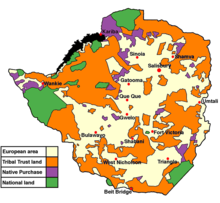
Racial segregation
[11] A mass marriage of Han Chinese officers and officials to Manchu women numbering 1,000 couples was arranged by Prince Yoto and Hongtaiji in 1632 to promote harmony between the two ethnic groups.
From 1952, and even more so after the triumphant visit of King Baudouin to the colony in 1955, Governor-General Léon Pétillon (1952–1958) worked to create a "Belgian-Congolese community", in which Black and White people were to be treated as equals.
[22] Regardless, anti-miscegenation laws remained in place, and between 1959 and 1962 thousands of mixed-race Congolese children were forcibly deported from the Congo by the Belgian government and the Catholic Church and taken to Belgium.
[24] The colonial law of 1865 allowed Arab and Berber Algerians to apply for French citizenship only if they abandoned their Muslim identity; Azzedine Haddour argues that this established "the formal structures of a political apartheid".
[37] In the middle of the 19th century, J. J. Benjamin wrote about the lives of Persian Jews: …they are obliged to live in a separate part of town…; for they are considered as unclean creatures… Under the pretext of their being unclean, they are treated with the greatest severity, and should they enter a street, inhabited by Mussulmans, they are pelted by the boys and mobs with stones and dirt… For the same reason, they are prohibited to go out when it rains; for it is said the rain would wash dirt off them, which would sully the feet of the Mussulmans… If a Jew is recognized as such in the streets, he is subjected to the greatest insults.
The passers-by spit in his face, and sometimes beat him… unmercifully… If a Jew enters a shop for anything, he is forbidden to inspect the goods… Should his hand incautiously touch the goods, he must take them at any price the seller chooses to ask for them...
As an immediate consequence of the introduction of the 'provvedimenti per la difesa della razza' (norms for the defence of the race), many of the best Italian scientists quit their jobs, and some of them also left Italy.
[44] To preserve the so-called purity of the German blood, after the war began, the Nazis extended the race defilement law to include all foreigners (non-Germans).
In an effort to split the Polish people's identity, they attempted to establish ethnic divisions of Kashubians and Gorals (Goralenvolk), based on these groups' alleged "Germanic component".
During the 1930s and 1940s, Jews in Nazi-controlled states were forced to wear something that identified them as Jewish, such as a yellow ribbon or a star of David, and along with Romas (Gypsies), they were subjected to discrimination by the racial laws.
[47][48] Although Nazi Germany also used forced laborers from Western Europe, Poles, along with other Eastern Europeans viewed as racially inferior,[49] were subject to deeper discriminatory measures.
While the treatment of factory workers or farm hands often varied depending on the individual employer, Polish laborers, as a rule, were compelled to work longer hours for lower wages than Western Europeans – in many cities, they were forced to live in segregated barracks behind barbed wire.
When the labour movement took hold in Canada near the end of the 19th century, workers began organizing and forming trade unions with the aim of improving the working conditions and quality of life for employees.
As early as 1949, the Youth League of the African National Congress (ANC) advocated the ending of apartheid and suggested fighting against racial segregation by various methods.
During the following decades, hundreds of anti-apartheid actions occurred, including those of the Black Consciousness Movement, students' protests, labor strikes, and church group activism etc.
[64] In the reception to honor his success at the 1936 Summer Olympics, Jesse Owens was not permitted to enter through the main doors of the Waldorf Astoria New York and instead forced to travel up to the event in a freight elevator.
[65] The first black Academy Award recipient, actress Hattie McDaniel, was not permitted to attend the premiere of Gone with the Wind at Loew's Grand Theatre in Atlanta because of Georgia's segregation laws.
[73][74] Although their one-year prison sentence was suspended, in 1963 they sought the assistance of the American Civil Liberties Union, which filed an appeal on their behalf that eventually found its way to the United States Supreme Court.
Many of their efforts were acts of non-violent civil disobedience aimed at disrupting the enforcement of racial segregation rules and laws, such as refusing to give up a seat in the black part of the bus to a white person (Rosa Parks), or holding sit-ins at all-white diners.
To justify the law, Nasser Fadhala, MP, a close ally of the government, said "bachelors also use these houses to make alcohol, run prostitute rings or to rape children and housemaids".
[83] Sadiq Rahma, technical committee head, who is a member of Al Wefaq, said: "The rules we are drawing up are designed to protect the rights of both the families and the Asian bachelors (..) these labourers often have habits which are difficult for families living nearby to tolerate (..) they come out of their homes half dressed, brew alcohol illegally in their homes, use prostitutes and make the neighbourhood dirty (..) these are poor people who often live in groups of 50 or more, crammed into one house or apartment," said Mr Rahma.
"[84] Bahrain Centre for Human Rights issued a press release condemning this decision as discriminatory and promoting negative racist attitudes towards migrant workers.
[83][85] Nabeel Rajab, then BCHR vice president, said: "It is appalling that Bahrain is willing to rest on the benefits of these people's hard work, and often their suffering, but that they refuse to live with them in equality and dignity.
"[83][85] Until 1965, racial segregation in schools, stores and most aspects of public life existed legally in Ontario, Quebec and Nova Scotia, and informally in other provinces such as British Columbia.
[101] Responding to the charges, the Slonim Haredim invited Sephardi girls to school, and added in a statement: "All along, we said it's not about race, but the High Court went out against our rabbis, and therefore we went to prison.
[118] In essence, non-Malays are treated as second-class citizens in Malaysia, facing many roadblocks and discrimination in matters such as economic freedom, education, healthcare and housing.
It stated that the high rates of emigration of non-bumiputera Malaysians from the country is driven by discriminatory policies that appear to favour Malays/Bumiputeras—such as providing exclusive additional assistance in starting businesses and educational opportunities.
[125][126] For centuries, the so-called Haratin lower class, mostly poor black Africans living in rural areas, have been considered natural slaves by white Moors of Arab/Berber ancestry.
[127][128][129] Although racial segregation was never made legal in the UK, pubs, workplaces, shops and other commercial premises operated a "colour bar" where non-white customers were banned from using certain rooms and facilities.
[154] The Blaxit movement promotes the expatriation of African-American people to Africa or Europe for cultural, racial, and economic reasons, in an attempt to deal with historic segregation.