Comparison of Prolog implementations
A comprehensive discussion of the most significant Prolog systems is presented in an article published in the 50-years of Prolog anniversary issue of the journal Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP).
Visual Prolog)[2] and sub-communities have developed around different implementations.
[2] Code that strictly conforms to the ISO-Prolog core language is portable across ISO-compliant implementations.
However, the ISO standard for modules is an extension which was not fully adopted in most Prolog systems.
[2][1] Factors that can adversely affect portability include: use of bounded vs. unbounded integer arithmetic, additional types such as string objects, advanced numeric types (rationals, complex), feature extensions such as Unicode, threads, and tabling.
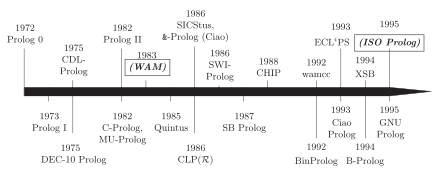
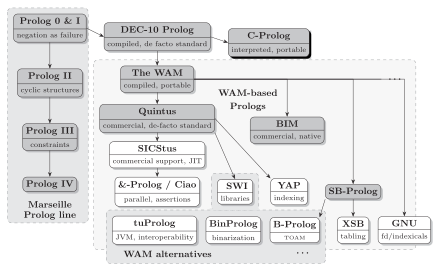
Systems with a dark gray background are not supported any more. Arrows denote influences and inspiration of systems. Quick legend: JIT = "Just in Time Compiler", JVM = "Java Virtual Machine", TOAM = "Tree-Oriented Abstract Machine"