Complex quadratic polynomial
A complex quadratic polynomial is a quadratic polynomial whose coefficients and variable are complex numbers.
Quadratic polynomials have the following properties, regardless of the form: When the quadratic polynomial has only one variable (univariate), one can distinguish its four main forms: The monic and centered form has been studied extensively, and has the following properties: The lambda form
is affine conjugate to the general form of the quadratic polynomial it is often used to study complex dynamics and to create images of Mandelbrot, Julia and Fatou sets.
is There is semi-conjugacy between the dyadic transformation (the doubling map) and the quadratic polynomial case of c = –2.
denotes the n-th iterate of the function
: so Because of the possible confusion with exponentiation, some authors write
can be marked by: so : Examples: The monic and centered form, sometimes called the Douady-Hubbard family of quadratic polynomials,[6] is typically used with variable
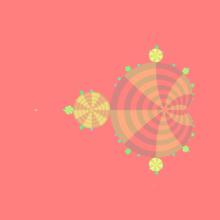
: When it is used as an evolution function of the discrete nonlinear dynamical system it is named the quadratic map:[7] The Mandelbrot set is the set of values of the parameter c for which the initial condition z0 = 0 does not cause the iterates to diverge to infinity.
on the dynamical plane such that the derivative vanishes: Since implies we see that the only (finite) critical point of
is an initial point for Mandelbrot set iteration.
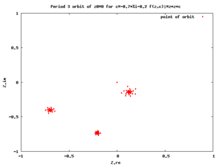
the critical point z = 0 is the center of symmetry of the Julia set Jc, so it is a convex combination of two points in Jc.
[9] In the Riemann sphere polynomial has 2d-2 critical points.
is the image of a critical point: Since we have So the parameter
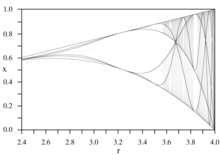
It acts as a sort of skeleton[10] of dynamical plane Example : level curves cross at saddle point, which is a special type of critical point.
Critical orbits are very important because every attracting periodic orbit attracts a critical point, so studying the critical orbits helps us understand the dynamics in the Fatou set.
[11][12][13] This orbit falls into an attracting periodic cycle if one exists.
[14] These curves create the skeleton (the dark lines) of a bifurcation diagram.
[15][16] One can use the Julia-Mandelbrot 4-dimensional (4D) space for a global analysis of this dynamical system.
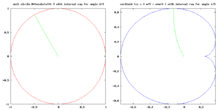
[17] In this space there are two basic types of 2D planes: There is also another plane used to analyze such dynamical systems w-plane: The phase space of a quadratic map is called its parameter plane.
This allows us to study the Mandelbrot and Julia sets combinatorially, replacing the dynamical plane by the unit circle, rays by angles, and the quadratic polynomial by the doubling modulo one map."
The two-dimensional dynamical plane can be treated as a Poincaré cross-section of three-dimensional space of continuous dynamical system.
[24][25] Dynamical z-planes can be divided into two groups: The extended complex plane plus a point at infinity On the parameter plane: The first derivative of
with respect to c is This derivative can be found by iteration starting with and then replacing at every consecutive step This can easily be verified by using the chain rule for the derivative.
This derivative is used in the distance estimation method for drawing a Mandelbrot set.
On the dynamical plane: At a fixed point
and referred to as the multiplier or the Lyapunov characteristic number.
Absolute value of multiplier is used to check the stability of periodic (also fixed) points.
At a nonperiodic point, the derivative, denoted by
, can be found by iteration starting with and then using This derivative is used for computing the external distance to the Julia set.
The Schwarzian derivative (SD for short) of f is:[26]