Continuous fever
The variation between maximum and minimum temperature in 24 hours is less than 1°C (1.5°F).
Diagnosis of continuous fever is usually based on the clinical signs and symptoms but some biological tests, chest X-ray and CT scan are also used.
[2] Typhoid fever is an example of continuous fever and it shows a characteristic step-ladder pattern, a step-wise increase in temperature with a high plateau.
[6] Antibiotics are also recommended for treating infectious diseases.
Antibiotics used in treatment of infectious diseases include chloramphenicol, cefotaxime, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin and amikacin.
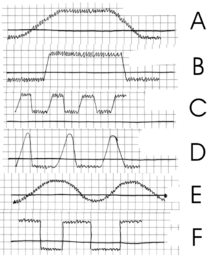
a) Fever continues
b) Fever continues to abrupt onset and remission
c) Remittent fever
d) Intermittent fever
e) Undulant fever
f) Relapsing fever