Birth control
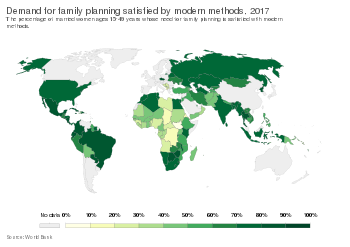
[20] In the developing world, women's earnings, assets, and weight, as well as their children's schooling and health, all improve with greater access to birth control.
[22] Birth control increases economic growth because of fewer dependent children, more women participating in the workforce, and/or less use of scarce resources.
[33] Hormonal contraception is available in a number of different forms, including oral pills, implants under the skin, injections, patches, IUDs and a vaginal ring.
[53] Male condoms are put on a man's erect penis and physically block ejaculated sperm from entering the body of a sexual partner.
[111] For a postpartum woman to be infertile (protected from pregnancy), their periods have usually not yet returned (not menstruating), they are exclusively breastfeeding the infant, and the baby is younger than six months.
[114] Emergency contraceptive methods are medications (sometimes misleadingly referred to as "morning-after pills")[116] or devices used after unprotected sexual intercourse with the hope of preventing pregnancy.
[135][136] Additionally, hormonal contraception can contribute to bone mineral density loss, impaired glucose metabolism, increased risk of venous thromboembolism.
[136][135] Comprehensive sex education and transparent discussion of birth control side effects and contraindications between healthcare provider and patient is imperative.
[151] The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle (c. 384–322 BC) recommended applying cedar oil to the womb before intercourse, a method which was probably only effective on occasion.
[151] A Hippocratic text On the Nature of Women recommended that a woman drink a copper salt dissolved in water, which it claimed would prevent pregnancy for a year.
[151] He rejected the use of superstition and amulets and instead prescribed mechanical methods such as vaginal plugs and pessaries using wool as a base covered in oils or other gummy substances.
[151] In medieval Europe, any effort to halt pregnancy was deemed immoral by the Catholic Church,[147] although it is believed that women of the time still used a number of birth control measures, such as coitus interruptus and inserting lily root and rue into the vagina.
[154] The Malthusian League, based on the ideas of Thomas Malthus, was established in 1877 in the United Kingdom to educate the public about the importance of family planning and to advocate for getting rid of penalties for promoting birth control.
[157][158] Sanger primarily advocated for birth control on the idea that it would prevent women from seeking unsafe abortions, but during her lifetime, she began to campaign for it on the grounds that it would reduce mental and physical defects.
[160] Once Sanger returned to the United States, she established a short-lived birth-control clinic with the help of her sister, Ethel Bryne, based in the Brownville section of Brooklyn, New York[162] in 1916.
[165] She helped fund research John Rock, and biologist Gregory Pincus that resulted in the first hormonal contraceptive pill, later called Enovid.
[166] The first human trials of the pill were done on patients in the Worcester State Psychiatric Hospital, after which clinical testing was done in Puerto Rico before Enovid was approved for use in the U.S..
[167][168] The newly approved birth control method was not made available to the participants after the trials, and contraceptives are still not widely accessible in Puerto Rico.
The ideology that surrounded birth control started to gain traction during the Progressive Era due to voluntary associations establishing community.
[174] Throughout the 1920s, Stopes and other feminist pioneers, including Dora Russell and Stella Browne, played a major role in breaking down taboos about sex.
[183] The restrictions on birth control in the Comstock laws were effectively rendered null and void by Supreme Court decisions Griswold v. Connecticut (1965)[184] and Eisenstadt v. Baird (1972).
[186] The Affordable Care Act, passed into law on March 23, 2010, under President Barack Obama, requires all plans in the Health Insurance Marketplace to cover contraceptive methods.
[188] In 1951, an Austrian-born American chemist, named Carl Djerassi at Syntex in Mexico City made the hormones in progesterone pills using Mexican yams (Dioscorea mexicana).
Meanwhile, Gregory Pincus and John Rock with help from the Planned Parenthood Federation of America developed the first birth control pills in the 1950s, such as mestranol/noretynodrel, which became publicly available in the 1960s through the Food and Drug Administration under the name Enovid.
The initiative has set a goal of increasing the number of users of modern birth control by 120 million women in the world's 69 poorest countries by 2020.
Ana Garner and Angela Michel have found that in these discussions men often attach reproductive rights to moral and political matters, as part of an ongoing attempt to regulate human bodies.
[199][200][201] The Greek Orthodox Church admits a possible exception to its traditional teaching forbidding the use of artificial contraception, if used within marriage for certain purposes, including the spacing of births.
[216] In the United States African American, Hispanic, and young women are disproportionately affected by limited access to birth control, as a result of financial disparity.
[226] Free the Pill, a collaboration between Advocates for Youth and Ibis Reproductive Health are working to bring birth control over-the-counter, covered by insurance with no age-restriction throughout the United States.
[30] A number of alterations of existing contraceptive methods are being studied, including a better female condom, an improved diaphragm, a patch containing only progestin, and a vaginal ring containing long-acting progesterone.







|
6%
12%
18%
24%
|
30%
36%
48%
60%
|
66%
78%
86%
No data
|