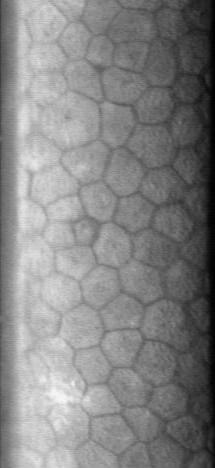
Corneal endothelium
The corneal endothelium are specialized, flattened, mitochondria-rich cells that line the posterior surface of the cornea and face the anterior chamber of the eye.
This honeycomb tiling scheme yields the greatest efficiency, in terms of total perimeter, of packing the posterior corneal surface with cells of a given area.
Excess hydration of the corneal stroma disrupts the normally uniform periodic spacing of Type I collagen fibrils, creating light scatter.
Both stromal light scatter and surface epithelial irregularity contribute to degraded optical performance of the cornea and can compromise visual acuity.
Partial palliation of these symptoms can sometimes be obtained through the instillation of topical hypertonic saline drops, use of bandage soft contact lenses, and/or application of anterior stromal micropuncture.
Compared to full-thickness keratoplasty, endokeratoplasty techniques are associated with shorter recovery times, improved visual results, and greater resistance to wound rupture.
In this form of endokeratoplasty, the diseased host endothelium and associated Descemet's membrane are removed from the central cornea, and in their place a specially harvested layer of healthy donor tissue is grafted.
This layer consists of posterior stroma, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium that has been dissected from cadaveric donor corneal tissue, typically using a mechanized (or "automated") instrument.