Coronavirus envelope protein
[2] In the beta and gamma groups, a conserved proline residue is found in the C-terminal region likely involved in targeting the protein to the Golgi.
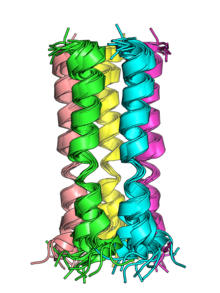
[2] The transmembrane helices of the E proteins of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 can oligomerize and have been shown in vitro to form pentameric structures with central pores that serve as cation-selective ion channels.
[5] Both viruses' E protein pentamers have been structurally characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
[10] In others, including mouse coronavirus[11] and SARS-CoV, E is not essential, though its absence reduces viral titer,[12] in some cases by introducing propagation defects or causing abnormal capsid morphology.
[14] There is good evidence that E is involved in inducing membrane curvature to create the typical spherical coronavirus virion.
[17] The cation leakage may disrupt ion homeostasis, alter membrane permeability, and modulate pH in the host cell, which may facilitate viral release.
[3][18] In SARS-CoV, mutations that disrupt E's ion channel function result in attenuated pathogenesis in animal models despite little effect on viral growth.
Protein-protein interactions between E and proteins in the host cell are best described in SARS-CoV and occur via the C-terminal PDZ domain binding motif.
[21] The conserved nature of the envelope protein among SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 variants has led it to be researched as a potential target for universal coronavirus vaccine development.