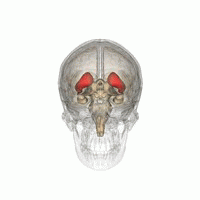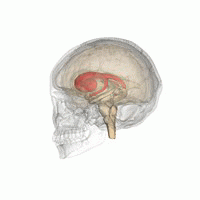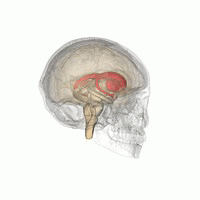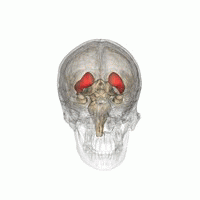
DaT scan
The scan principle is based on use of the radiopharmaceutical Ioflupane (123I) which binds to dopamine transporters (DaT).
[1] The signal from them is then detected by the use of single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) which uses special gamma-cameras to create a pictographic representation of the distribution of dopamine transporters in the brain.
These pills are important because they prevent the accumulation of radioactive substances in the thyroid gland.
The concentration of the substance increases, and then it is scanned by a gamma-camera, which is located around the patient's head.
The examination takes just a few hours, so patients do not need to stay in a hospital overnight, but they have to drink much more than they are used to and go to the toilet more often.