De novo peptide sequencing
[citation needed] When the backbone bonds cleave, six different types of sequence ions are formed as shown in Fig.
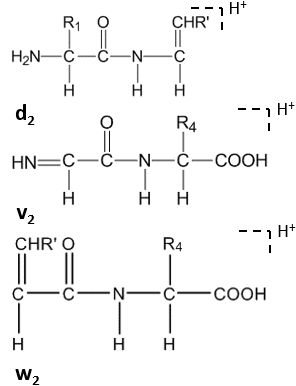
Further cleavage happens under high-energy CID at the side chain of C-terminal residues, forming dn, vn, wn-ions.
For this b-y ion pair, the sum of their subscripts is equal to the total number of amino acid residues in the unknown peptide.
[citation needed] In high energy CID, all different types of fragment ions can be observed but no losses of ammonia or water.
Find mass differences at 28 Da since b-ions can form a-ions by loss of CO. Look for b2-ions at low-mass end of the spectrum, which helps to identify yn-2-ions too.
[19][20][21][22] In the third method, graphical display of the data is applied, in which fragment ions that have the same mass differences of one amino acid residue are connected by lines.
This method could be helpful for manual de novo peptide sequencing, but doesn't work for high-throughput condition.
More recently, deep learning techniques have been applied to solve the de novo peptide sequencing problem.
The first breakthrough was DeepNovo, which adopted the convolutional neural network structure, achieved major improvements in sequence accuracy, and enabled complete protein sequence assembly without assisting databases[28] Subsequently, additional network structures, such as PointNet (PointNovo[29]), have been adopted to extract features from a raw spectrum.
It is based on 'spectrum graph' method and contains different scoring functions, and can be comparable on the running time and accuracy to "the popular state-of-the-art programs" PepNovo and NovoHMM.
A second program, CIDentify, which is a modified version by Alex Taylor of Bill Pearson's FASTA algorithm, can be applied to distinguish those uncertain similar candidates.
[citation needed] Mo et al. presented the MSNovo algorithm in 2007 and proved that it performed "better than existing de novo tools on multiple data sets".
[33] This algorithm can do de novo sequencing interpretation of LCQ, LTQ mass spectrometers and of singly, doubly, triply charged ions.
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is applied as a new way to solve de novo sequencing in a Bayesian framework.
Ma et al. described a new model and algorithm for de novo sequencing in PEAKS, and compared the performance with Lutefisk of several tryptic peptides of standard proteins, by the quadrupole time-of-flight (Q-TOF) mass spectrometer.
[35] PepNovo is a high throughput de novo peptide sequencing tool and uses a probabilistic network as scoring method.
Chi et al. presented pNovo+ in 2013 as a new de novo peptide sequencing tool by using complementary HCD and ETD tandem mass spectra.
[39] Pevtsov et al. compared the performance of the above five de novo sequencing algorithms: AUDENS, Lutefisk, NovoHMM, PepNovo, and PEAKS .
The improved accuracy, together with the increased amount of mass spectrometry data that are being generated, draws the interests of applying deep learning techniques to de novo peptide sequencing.
In 2017 Tran et al. proposed DeepNovo, the first deep learning based de novo sequencing software.
The benchmark analysis in the original publication demonstrated that DeepNovo outperformed previous methods, including PEAKS, Novor and PepNovo, by a significant margin.
This unnecessarily large spectrum representation, and the single-thread CPU usage in the original implementation, prevents DeepNovo from performing peptide sequencing in real time.
To further improve efficiency of de novo peptide sequencing models, Qiao et al. proposed PointNovo in 2020.
PointNovo is a python software implemented with the PyTorch framework [42] and it gets rid of the space consuming spectrum-vector-representation adopted by DeepNovo.
Comparing with DeepNovo, PointNovo managed to achieve better accuracy and efficiency at the same time by directly representing a spectrum as a set of m/z and intensity pairs.