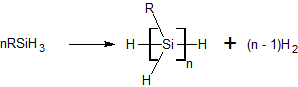
Dehydrogenative coupling of silanes
[3] Using Cp2Ti(OPh)2 as a catalyst, the dehydrogenative coupling of phenylsilane in the presence of vinyltriethoxysilane produces a polysilane terminated with a triethoxysilylvinyl group.
[6] Dehydrogenative coupling of primary silanes using Wilkinson's catalyst is slow and dependent on the removal of H2 product.
[10] Tertiary silanes may also be dehydrogenatively coupled to aromatic rings with the use of the catalyst TpMe2Pt(Me)2H (TpMe2 = hydrido tris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate).
For example, this platinum catalyst can be used to react triethyl silane with benzene to produce phenyltriethylsilane, with the elimination of hydrogen gas.
This is a terrific catalyst because it eliminates the need for a hydrogen acceptor, something which is normally required for the silation of a C-H bond.
[11] Some methods used to produce polysilanes are polymerization of masked dislenes,[12] electroreduction of dichlorosilanes,[13] 1H and 29Si NMR spectroscopy can sometimes be used to help identify and characterize products from these reactions.