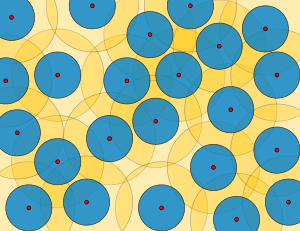
Delone set
If (M, d) is a metric space, and X is a subset of M, then the packing radius, r, of X is half of the smallest distance between distinct members of X.
[1][2] As the most restrictive of the definitions above, ε-nets are at least as difficult to construct as ε-packings, ε-coverings, and Delone sets.
Har-Peled & Raichel (2013) describe an algorithmic paradigm that they call "net and prune" for designing approximation algorithms for certain types of geometric optimization problems defined on sets of points in Euclidean spaces.
As they show, this paradigm can be used to construct fast approximation algorithms for k-center clustering, finding a pair of points with median distance, and several related problems.
A hierarchical system of nets, called a net-tree, may be used in spaces of bounded doubling dimension to construct well-separated pair decompositions, geometric spanners, and approximate nearest neighbors.
[8] The Voronoi cells of symmetric Delone sets form space-filling polyhedra called plesiohedra.