Polydimethylsiloxane
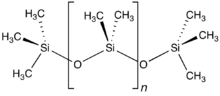
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), also known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, is a silicone polymer with a wide variety of uses, from cosmetics to industrial lubrication and passive daytime radiative cooling.
The applications of PDMS range from contact lenses and medical devices to elastomers; it is also present in shampoos (as it makes hair shiny and slippery), food (antifoaming agent), caulk, lubricants and heat-resistant tiles.
For medical and domestic applications, a process was developed in which the chlorine atoms in the silane precursor were replaced with acetate groups.
In a similar manner, precursors with three methyl groups can be used to limit molecular weight, since each such molecule has only one reactive site and so forms the end of a siloxane chain.
Well-defined PDMS with a low polydispersity index and high homogeneity is produced by controlled anionic ring-opening polymerization of hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane.
The polymer is manufactured in multiple viscosities, from a thin pourable liquid (when n is very low), to a thick rubbery semi-solid (when n is very high).
PDMS is viscoelastic, meaning that at long flow times (or high temperatures), it acts like a viscous liquid, similar to honey.
But the process that is described above is only relevant when cross-linking is present; when it is not, the polymer PDMS cannot shift back to the original state even when the load is removed, resulting in a permanent deformation.
However, if the same PDMS is poured into a spherical mold and allowed to cure (short flow time), it will bounce like a rubber ball.
[6] This enables PDMS to become a good substrate that can easily be integrated into a variety of microfluidic and microelectromechanical systems.
[7][8] Specifically, the determination of mechanical properties can be decided before PDMS is cured; the uncured version allows the user to capitalize on myriad opportunities for achieving a desirable elastomer.
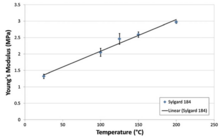
Overall PDMS has a low elastic modulus which enables it to be easily deformed and results in the behavior of a rubber.
[16] PDMS, in a modified form, is used as an herbicide penetrant[17] and is a critical ingredient in water-repelling coatings, such as Rain-X.
[18] Dimethicone is used in the active silicone fluid in automotive viscous limited slip differentials and couplings.
PDMS is a common surface material used in passive daytime radiative cooling as a broadband emitter that is high in solar reflectivity and heat emissivity.
[19][20][21] As a daytime radiative cooling surface, PDMS has also been tested to improve solar cell efficiency.
[23] The process of soft lithography consists of creating an elastic stamp, which enables the transfer of patterns of only a few nanometers in size onto glass, silicon or polymer surfaces.
Moreover, compared to other materials, it possesses superior optical properties, allowing for minimal background and autofluorescence during fluorescent imaging.
[25] In biomedical (or biological) microelectromechanical systems (bio-MEMS), soft lithography is used extensively for microfluidics in both organic and inorganic contexts.
Activated dimethicone, a mixture of polydimethylsiloxanes and silicon dioxide (sometimes called simethicone), is often used in over-the-counter drugs as an antifoaming agent and carminative.
Its physical properties of low elastic modulus and hydrophobicity have been used to clean micro and nano pollutants from contact lens surfaces more effectively than multipurpose solution and finger rubbing; the researchers involved call the technique PoPPR (polymer on polymer pollution removal) and note that it is highly effective at removing nanoplastic that has adhered to lenses.
This is thought to be due not to suffocation (or poisoning), but to its blocking water excretion, which causes insects to die from physiological stress either through prolonged immobilisation or disruption of internal organs such as the gut.
[47] According to Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, no "marked harmful effects on organisms in the environment" have been noted for siloxanes.