Dominican Republic
[46][47] By the time of the Treaty of Ryswick in 1697, which ceded the western one-third of the island to France, the population of Santo Domingo consisted of a few thousand whites, approximately 30,000 black slaves, and a few Taínos.
[54] In 1838, Juan Pablo Duarte founded a secret society called La Trinitaria, which sought the complete independence of Santo Domingo without any foreign intervention.
In November–December 1849, Dominican seamen raided the Haitian coasts, plundered seaside villages, as far as Dame Marie, and butchered crews of captured enemy ships.
In 1861, after imprisoning, exiling, and executing many of his opponents and due to political and economic reasons, Santana asked Queen Isabella II of Spain to retake control of the Dominican Republic.
Furthermore, the national government was bankrupt and, unable to pay its debts to European creditors, faced the threat of military intervention by France, Germany, and Italy.
[79] United States President Theodore Roosevelt sought to prevent European intervention, largely to protect the routes to the future Panama Canal.
The military government established by the U.S. under the Navy and Marine Corps on November 29, led by Vice Admiral Harry Shepard Knapp, was widely repudiated by the Dominicans, but organized resistance ceased.
During the course of the war, German U-boats torpedoed and sank two Dominican merchant vessels—the San Rafael off the coast of Jamaica, and the Presidente Trujillo off Fort-de-France—along with four other Dominican-manned ships in the Caribbean.
[99] The United States severed diplomatic relations with the Dominican Republic on August 26, 1960, and in January 1961 suspended the export of trucks, parts, crude oil, gasoline and other petroleum products.
On November 18, 1961, as a planned coup became more evident, U.S. Secretary of State Dean Rusk issued a warning that the US would not "remain idle" if the Trujillos attempted to "reassert dictatorial domination".
It was, however, praised for an ambitious infrastructure program, which included construction of large housing projects, sports complexes, theaters, museums, aqueducts, roads, highways, and the massive Columbus Lighthouse, completed in 1992 during a later tenure.
[113][114] He was succeeded by the opposition candidate Luis Abinader in the 2020 election (weeks after protests erupted in the country against Medina's government), marking the end to 16 years in power of the centre-left Dominican Liberation Party (PLD).
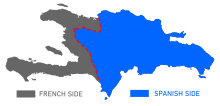
[117] The Dominican Republic comprises the eastern five-eighths of Hispaniola, the second-largest island in the Greater Antilles, with the Atlantic Ocean to the north and the Caribbean Sea to the south.
The most northerly is the Cordillera Septentrional ("Northern Mountain Range"), which extends from the northwestern coastal town of Monte Cristi, near the Haitian border, to the Samaná Peninsula in the east, running parallel to the Atlantic coast.
Three large groups own 75% of the land: the State Sugar Council (Consejo Estatal del Azúcar, CEA), Grupo Vicini, and Central Romana Corporation.
The largest telecommunications company is Claro – part of Carlos Slim's América Móvil – which provides wireless, landline, broadband, and IPTV services.
[148] In November 2009, the Dominican Republic became the first Latin American country to pledge to include a "gender perspective" in every information and communications technology (ICT) initiative and policy developed by the government.
[161] According to recent genealogical DNA studies of the Dominican population, the genetic makeup is predominantly European and Sub-Saharan African, with a lesser degree of Indigenous ancestry.
[198] Recent immigration as well as proselytizing efforts have brought in other religious groups, with the following shares of the population: Spiritist: 2.2%,[199] The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints: 1.3%,[200] Buddhist: 0.1%, Baháʼí: 0.1%,[199] Chinese Folk Religion: 0.1%,[199] Islam: 0.02%, Judaism: 0.01%.
During the same time, Protestant Evangelicalism began to gain wider support "with their emphasis on personal responsibility and family rejuvenation, economic entrepreneurship, and biblical fundamentalism".
[206] In addition, there are descendants of immigrants who came from other Caribbean islands, including St. Kitts and Nevis, Antigua, St. Vincent, Montserrat, Tortola, St. Croix, St. Thomas, and Guadeloupe.
Puerto Rican, and to a lesser extent, Cuban immigrants fled to the Dominican Republic from the mid-1800s until about 1940 due to a poor economy and social unrest in their respective home countries.
[230] Due to the lack of basic amenities and medical facilities in Haiti a large number of Haitian women, often arriving with several health problems, cross the border to Dominican soil.
[236] The government of the Dominican Republic invested a total of $16 billion pesos in health services offered to foreign patients in 2013–2016, according to official data, which includes medical expenses in blood transfusion, clinical analysis, surgeries and other care.
[237] According to official reports, the country spends more than five billion Dominican pesos annually in care for pregnant women who cross the border ready to deliver.
The Taíno people relied heavily on the mahogany and guano (dried palm tree leaf) to put together crafts, artwork, furniture, and houses.
Lately, with the rise in tourism and increasing popularity as a Caribbean vacation destination, architects in the Dominican Republic have now begun to incorporate cutting-edge designs that emphasize luxury.
Other favorite Dominican foods include chicharrón, yuca, casabe, pastelitos (empanadas), batata, ñame, pasteles en hoja, chimichurris, and tostones.
[293] Other notable baseball players born in the Dominican Republic are José Bautista, Robinson Canó, Rico Carty, Bartolo Colón, Nelson Cruz, Edwin Encarnación, Cristian Javier, Ubaldo Jiménez, Francisco Liriano, Plácido Polanco, Albert Pujols, Hanley Ramírez, Manny Ramírez, José Reyes, Alfonso Soriano, Sammy Sosa, Juan Soto, Fernando Tatís Jr., Miguel Tejada, Framber Valdez, and Elly De La Cruz.
Tito Horford, his son Al, Felipe Lopez, and Francisco Garcia are among the Dominican-born players currently or formerly in the National Basketball Association (NBA).