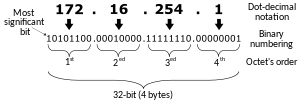
Dot-decimal notation
It consists of a string of decimal numbers, using the full stop (dot) as a separation character.
[2] In computer networking, Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) addresses are commonly written using the quad-dotted notation of four decimal integers, ranging from 0 to 255 each.
[5] Dot-decimal notation is a presentation format for numerical data expressed as a string of decimal numbers each separated by a full stop.
[6] The first mention of this format in RFC documents was in RFC 780 for the Mail Transfer Protocol published May 1981, in which the IP address was supposed to be enclosed in brackets or represented as a 32-bit decimal integer prefixed by a pound sign.
[8] An IETF draft intended to define textual representation of IP addresses expired without further activity.
[6] This means addresses with a component written with a leading zero digit may be interpreted differently in programs that do or do not recognize such formats.
The UDC additionally codes works with multiple dot-decimal topics, separated by colons.
For instance, the AO Foundation/Orthopaedic Trauma Association (AO/OTA) classification generates numeric codes for describing broken toes.