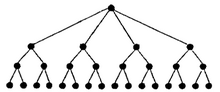
Doubly logarithmic tree
In computer science, a doubly logarithmic tree is a tree where each internal node of height 1, the tree layer above the leaves, has two children, and each internal node of height
children.
Each child of the root contains
leaves.
[1] The number of children at a node from each leaf to root is 0,2,2,4,16, 256, 65536, ... (sequence A001146 in the OEIS) A similar tree called a k-merger is used in Prokop et al.'s cache oblivious Funnelsort to merge elements.