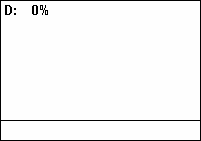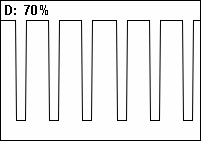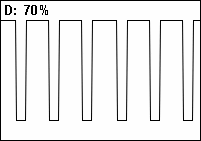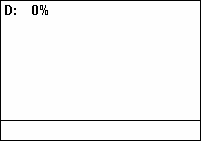
Duty cycle
The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period.
Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron.
[6] As a ratio, duty cycle is unitless and may be given as decimal fraction and percentage alike.
For example, if a motor runs for one out of 100 seconds, or 1/100 of the time, then, its duty cycle is 1/100, or 1 percent.
[10] Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is used in a variety of electronic situations, such as power delivery and voltage regulation.
In the printer / copier industry, the duty cycle specification refers to the rated throughput (that is, printed pages) of a device per month.
In a welding power supply, the maximum duty cycle is defined as the percentage of time in a 10-minute period that it can be operated continuously before overheating.
[11] The concept of duty cycles is also used to describe the activity of neurons and muscle fibers.