ECHELON
[2][3][4] Created in the late 1960s to monitor the military and diplomatic communications of the Soviet Union and its Eastern Bloc allies during the Cold War, the ECHELON project became formally established in 1971.
[7] The UKUSA intelligence community was assessed by the European Parliament (EP) in 2000 to include the signals intelligence agencies of each of the member states: Former NSA analyst Perry Fellwock, under the pseudonym Winslow Peck, first blew the whistle on ECHELON to Ramparts in 1972,[21] when he revealed the existence of a global network of listening posts and told of his experiences working there.
[22] In 1982, investigative journalist and author James Bamford wrote The Puzzle Palace, an in-depth history of the NSA and its practices, which notably leaked the existence of the eavesdropping operation Project SHAMROCK.
"[25] Also in 1988, an article titled "Somebody's Listening", written by investigative journalist Duncan Campbell in the New Statesman, described the signals intelligence gathering activities of a program code-named "ECHELON".
[27] Two years later, Hager's book was cited by the European Parliament in a report titled "An Appraisal of the Technology of Political Control" (PE 168.184).
[38] The European Parliament stated in its report that the term ECHELON is used in a number of contexts, but that the evidence presented indicates that it was the name for a signals intelligence collection system.
[7] The report concludes that, on the basis of information presented, ECHELON was capable of interception and content inspection of telephone calls, fax, e-mail and other data traffic globally through the interception of communication bearers including satellite transmission, public switched telephone networks (which once carried most Internet traffic), and microwave links.
Former NSA employee Margaret Newsham said that she worked on the configuration and installation of software that makes up the ECHELON system while employed at Lockheed Martin, from 1974 to 1984 in Sunnyvale, California, in the United States, and in Menwith Hill, England, in the UK.
[41][42] Britain's The Guardian newspaper summarized the capabilities of the ECHELON system as follows: A global network of electronic spy stations that can eavesdrop on telephones, faxes and computers.
[44][45] First revealed by the European Parliament report (p. 54 ff)[7] and confirmed later by the Edward Snowden disclosures the following ground stations presently have, or have had, a role in intercepting transmissions from Satellite and other means of communication:[7]
From 1970 to 1971, the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) of Britain began to operate a secret signal station at Morwenstow, near Bude in Cornwall, England.
Soon afterwards, the US National Security Agency (NSA) built a second signal station at Yakima, near Seattle, for the interception of satellite communications over the Pacific Ocean.
Testimony before the European Parliament indicated that separate but similar UKUSA systems are in place to monitor communication through undersea cables, microwave transmissions, and other lines.
[65] Alleged examples of espionage conducted by the members of the "Five Eyes" include: The first United States satellite ground station for the ECHELON collection program was built in 1971 at a military firing and training center near Yakima, Washington.
[39] In 1999 the Australian Senate Joint Standing Committee on Treaties was told by Professor Desmond Ball that the Pine Gap facility was used as a ground station for a satellite-based interception network.
The original purpose of the network was to monitor the telemetry from 1970s Soviet weapons, air defence and other radars' capabilities, satellites' ground stations' transmissions and ground-based microwave communications.
[78] However, later German media reports contradicted this story, as it was revealed that the American patent in question was actually filed three years before the alleged wiretapping was said to have taken place.






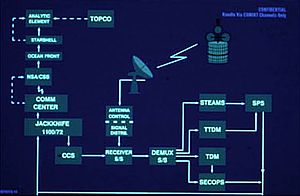
TOPCO = Terminal Operations Control
CCS = Computer Control Subsystem
STEAMS = System Test, Evaluation, Analysis, and Monitoring Subsystem
SPS = Signal Processing Subsystem
TTDM = Teletype Demodulator