EarSketch
Its core purpose is to teach coding in two widely used languages, Python and JavaScript, through music composing and remixing.
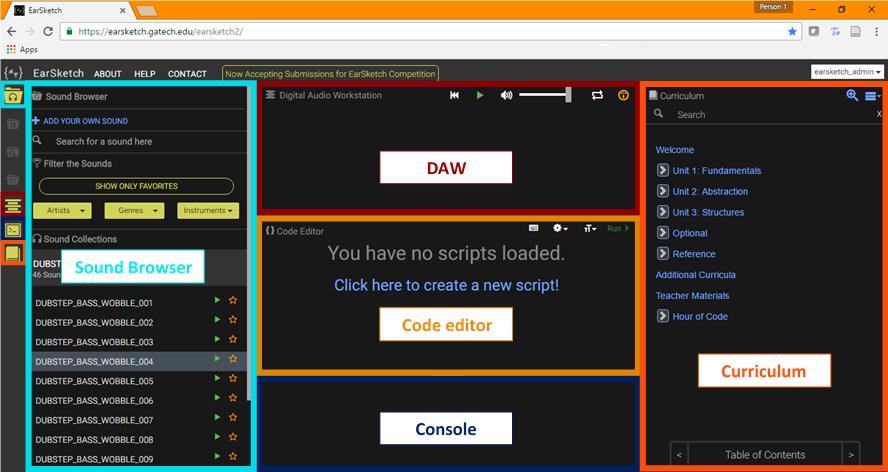
EarSketch comprises different elements: a curriculum, a digital audio workstation (or DAW), a code editor, console, and a sound browser.
A study conducted at Georgia Tech showed statistically significant results in this domain: students who study with EarSketch have been shown to make progress both in content knowledge and attitude towards CS (self-confidence, motivation, intent to persist, etc.).
The name EarSketch originated in a different project from co-creators Freeman and Magerko focused on collaborative composition and music analysis via drawing.
Though sketching is no longer a focus of EarSketch, the environment does offer drawing and animation features through P5.
The initial version of EarSketch, released in 2012, was built inside of REAPER, a commercial digital audio workstation with extensive support for coding via the ReaScript API for Python and the JavaScript plugin authoring architecture.
As the project grew, the Reaper-based version of EarSketch was eventually retired due to its dependence on commercial software, the inability of the team to create an integrated user interface to author code, view musical results in the DAW, find sounds, and challenges installing the software in school computer labs.
EarSketch is a web application, and when opening a session, users see different sections: the curriculum, the code editor, the console, the Digital Audio Workstation, and the browser.
The curriculum is aligned with AP Computer Science Principles but can be used in any introductory programming course.
With code commands, the user will add sound samples in these tracks, as well as effects, such as volume changes, reverberation, delay, etc.