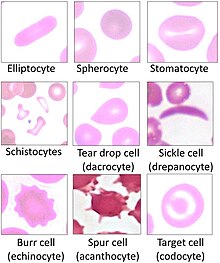
Echinocyte
Echinocyte (from the Greek word echinos, meaning 'hedgehog' or 'sea urchin'), in human biology and medicine, refers to a form of red blood cell that has an abnormal cell membrane characterized by many small, evenly spaced thorny projections.
Echinocytes also exhibit central pallor, or lightening of color in the center of the cell under Wright staining.
[6] These cells were also shown to develop in vivo during hemodialysis, and disappear at the end of the procedure.
The level of echinocytosis appeared to be related to the increase in blood viscosity that occurs during hemodialysis.
[8] Alternating electric current produces modifications in the membranes of red blood cells, attributed to a higher permeability to water and a decreased tonicity, leading to the transformation into echinocytes.