Enterprise modelling
Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.
[2] It deals with the process of understanding an organization and improving its performance through creation and analysis of enterprise models.
An enterprise includes a number of functions and operations such as purchasing, manufacturing, marketing, finance, engineering, and research and development.
The enterprise of interest are those corporate functions and operations necessary to manufacture current and potential future variants of a product.
For example, the use of networked computers to trigger and receive replacement orders along a material supply chain is an example of how information technology is used to coordinate manufacturing operations within an enterprise.
For this purpose they include abstractions suitable for strategic planning, organisational (re-) design and software engineering.
At the same time they should offer abstractions that help with designing information systems which are well integrated with a company's long term strategy and its organisation.
A next step in IS modelling was taken by CODASYL, an IT industry consortium formed in 1959, who essentially aimed at the same thing as Young and Kent: the development of "a proper structure for machine independent problem definition language, at the system level of data processing".
Specific methods for enterprise modelling in the context of Computer Integrated Manufacturing appeared in the early 1980s.
[12] Thomas Naylor (1970) defined a (simulation) model as "an attempt to describe the interrelationships among a corporation's financial, marketing, and production activities in terms of a set of mathematical and logical relationships which are programmed into the computer.
"[13] These interrelationships should according to Gershefski (1971) represent in detail all aspects of the firm including "the physical operations of the company, the accounting and financial practices followed, and the response to investment in key areas"[14] Programming the modelled relationships into the computer is not always necessary: enterprise models, under different names, have existed for centuries and were described, for example, by Adam Smith, Walter Bagehot, and many others.
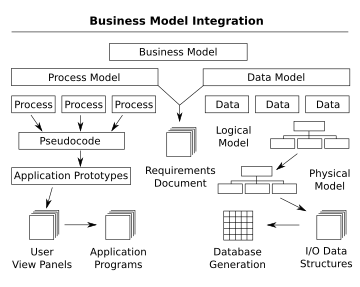
The main concept in this modelling perspective is the process, this could be a function, transformation, activity, action, task etc.
The data model will normally consist of entity types, attributes, relationships, integrity rules, and the definitions of those objects.
Change management programs are typically involved to put the improved business processes into practice.
It encompasses the application of knowledge, principles, and disciplines related to the analysis, design, implementation and operation of all elements associated with an enterprise.
In the context of software development a specific field of enterprise engineering has emerged, which deals with the modelling and integration of various organizational and technical parts of business processes.
[28] Here Enterprise modelling can be part of the early, middle and late information system development life cycle.
This framework defines in a series of reference models, how to organize the structure and views associated with an Enterprise Architecture.
These reference model can be constructed in layers, and offer a foundation for the analysis of service components, technology, data, and performance.
The economic model is a simplified framework designed to illustrate complex processes, often but not always using mathematical techniques.
This complexity can be attributed to the diversity of factors that determine economic activity; these factors include: individual and cooperative decision processes, resource limitations, environmental and geographical constraints, institutional and legal requirements and purely random fluctuations.
In the domain of enterprise architecture, an ontology is an outline or a schema used to structure objects, their attributes and relationships in a consistent manner.
While the language example given earlier dealt with the area of information systems and design, other ontologies may be defined for processes, methods, activities, etc., within an enterprise.