Environmental impacts of lithium-ion batteries
Applications for this battery were limited by the high prices of titanium and the unpleasant scent that the reaction produced.
[3] According to researchers at Volkswagen, there are about 14 million tons of lithium left, which corresponds to 165 times the production volume in 2018.
[4] Lithium is extracted on a commercial scale from three principal sources: salt brines, lithium-rich clay, and hard-rock deposits.
[5] Whereas hard-rock deposits and lithium-rich clays both require relatively typical mining methods, involving heavy machinery.
It is worth noting that in general, this brine being evaporated has a very high salinity, making the water unusable for any agricultural or human consumption.
[7] These production facilities are responsible for the bulk of the atmospheric pollution caused by brine extraction sites, releasing harmful gasses such as Sulphur dioxide into the air.
[11][12] In Tagong, a small town in Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture China, there are records of dangerous chemicals such as hydrochloric acid leaking into the Liqi River from the nearby lithium mining facilities.
[13] After further investigation, researchers found that this may have been caused by leakage of evaporation pools that sit for months and sometimes even years.
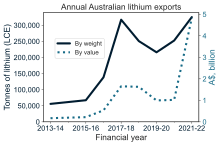
These deposits are most commonly found in Australia, the world's largest producer of lithium,[5] through spodumene ores.
[5] As a result, hard-rock deposit extraction sites are continuing to be created and used even though salt brines are much more common to find and typically bear a smaller environmental impact.
There are several minerals within clay that contain lithium such as, lepidolite, hectorite, masutomilite, zinnwaldite, swinefordite, cookeite, and jadarite.
[16] Some types of Lithium-ion batteries such as NMC contain metals such as nickel, manganese and cobalt, which are toxic and can contaminate water supplies and ecosystems if they leach out of landfills.
[17] Additionally, fires in landfills or battery-recycling facilities have been attributed to inappropriate disposal of lithium-ion batteries.
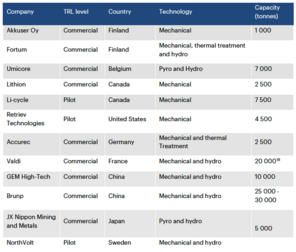
By recycling the batteries, emissions and energy consumption can be reduced as less lithium would need to be mined and processed.
[22] That being said, Hydrometallurgy does achieve a very high purity in the recovered metals, making it a good recycling method.
Electric vehicles have seen a massive increase in sales in recent years with over 90% of all global car markets having EV incentives in place as of 2019.