Binary expression tree
These trees can represent expressions that contain both unary and binary operators.
This restricted structure simplifies the processing of expression trees.
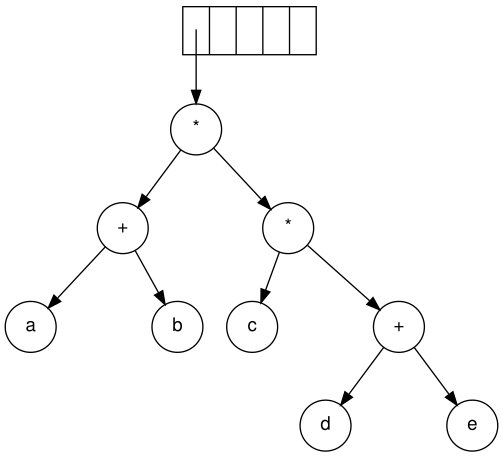
The input in postfix notation is: a b + c d e + * * Since the first two symbols are operands, one-node trees are created and pointers to them are pushed onto a stack.
Some of the common operators are × (multiplication), ÷ (division), + (addition), − (subtraction), ^ (exponentiation), and - (negation).
Boolean expressions use true and false as constant values, and the operators include