Glossary of astronomy
This glossary of astronomy is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to astronomy and cosmology, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.
Astronomy is concerned with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth.
The field of astronomy features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon.
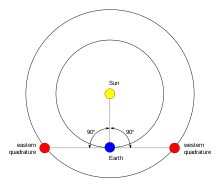
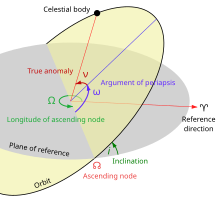
Also visual brightness (V).Also argument of perifocus or argument of pericenter.Also the north node.Also exobiology.Also planetary geology.Also celestial body.Also spelled astronomical catalog.Also celestial object.Also obliquity.Also critical velocity or critical rotation.Also spelled circumstellar disk.Also compact object.Also space dust.Also cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR).Also break-up velocity.Also meridian transit.Also the south node.Also distant detached object and extended scattered disc object.Also ecliptic plane or plane of the ecliptic.Also elliptic orbit.Also exoplanet.Also the Cusp of Aries.Also background stars.Also galactic core or galactic center.Also galactic year or cosmic year.Also group of galaxies (GrG).Also geosynchronous equatorial orbit (GEO).Also the Hill radius.Also Laplace's invariable plane or the Laplace plane.Also Keplerian orbit.Also Edgeworth–Kuiper belt.Also Lagrange point, libration point, or L-point.Also the Lenakaeia Supercluster, Local Supercluster, or Local SCI.Also Moon phase.Also the Northward equinox.Also shooting star or falling star.Also normalized polar moment of inertia.Also minor moon or minor natural satellite.Also MK classification.Also rise width.Also stellar association.Also bare eye or unaided eye.Also moon.Also arc length.Also the Öpik–Oort cloud.Also orbital plot.Also revolution period.Also simply called space.Also pericenter.Also reference plane.Also planetary object.Also sometimes called planetology.Also planemo or planetary body.Also gravitational primary, primary body, or central body.Also direct motion.Also quasi-stellar radio sourceAlso interstellar planet, nomad planet, orphan planet, and starless planet.Also twinkling.Also major semi-axis.Also southward equinox.Also positional astronomy.Also standard acceleration due to gravity.Also spelled star catalog.Also stellar system.Also stellar envelope.Also spectral classification.Also simply stellar model.Also substar.Also synodic rotation period.Also tidal acceleration.Also Tisserand parameter.Also the Johnson system or Johnson–Morgan system.Also the Local Supercluster (LSC or LC).An acronym of X-ray bright optically normal galaxy.










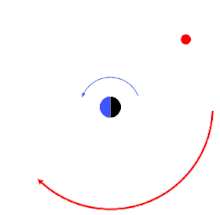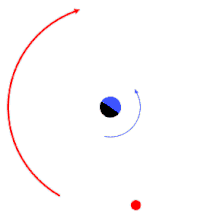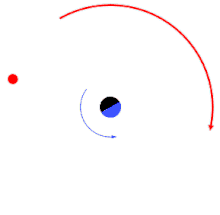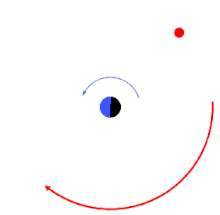
orbital resonance between the orbital periods of two planets (small bodies), both of which are orbiting a large central star. The inner planet completes two revolutions in the time it takes the outer planet to complete one.