Glossary of genetics and evolutionary biology
This glossary of genetics and evolutionary biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in the study of genetics and evolutionary biology, as well as sub-disciplines and related fields, with an emphasis on classical genetics, quantitative genetics, population biology, phylogenetics, speciation, and systematics.
It has been designed as a companion to Glossary of cellular and molecular biology, which contains many overlapping and related terms; other related glossaries include Glossary of biology and Glossary of ecology.
Also called functionalism.Also called geographic speciation, vicariance, vicariant speciation, and dichopatric speciation.Also called an ancestral character, primitive character, or primitive trait.Also called positive assortative mating and homogamy.Also testcrossing.Also simply called the Dobzhansky–Muller model.Also called a monophyletic group.Also convergence.Also crossing and outbreeding.Also Darwinian theory and Darwinian evolution.Also derived character, advanced character, and advanced trait.Denoted in shorthand with the somatic number 2n.Also positive selection.Also negative assortative mating and heterogamy.Also diversifying selection.Also divergence.Also gene amplification.Sometimes used interchangeably with genetic variation.Also called allelic drift or the Sewall Wright effect.Also genetic draft and the hitchhiking effect.Also DNA testing and genetic screening.Sometimes used interchangeably with genetic variation.Sometimes used interchangeably with genetic diversity and genetic variability.Denoted in shorthand with the somatic number n.Also inheritance.Also hybrid vigor and outbreeding enhancement.Also homologs or homologues.Also lateral gene transfer (LGT).Also incrossing.Also introgressive hybridization.Also called the last universal cellular ancestor or simply the last universal ancestor.Also pedigree.Also called lineage-branching.Plural loci.Also environmental genomics, ecogenomics, and community genomics.Also point-nonsense mutation.Also nonsynonymous substitution or replacement mutation.Also ontogenesis and morphogenesis.Also outcrossing or crossbreeding.Also maximum parsimony.Also polypheny.Also multifurcation.Also genetic bottleneck.Also prosposito for a male subject and prosposita for a female subject.Also neotype.Also purebreed.Also complex trait.Also refuge.Also called network evolution.Also reversion.Also Fisherian runaway.Also selection pressure.Denoted in shorthand with a + superscript.


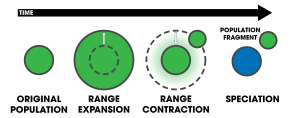

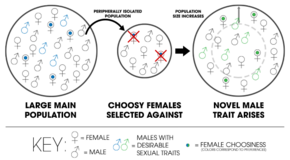


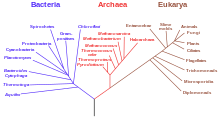
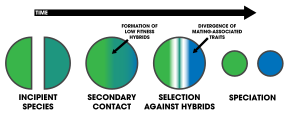
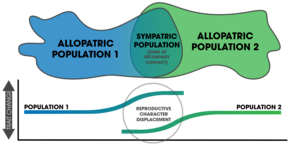

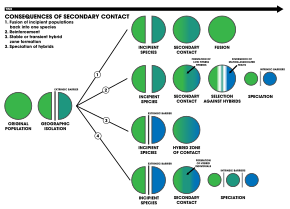
1. An extrinsic barrier separates a species population into two but they come into contact before reproductive isolation is sufficient to result in speciation. The two populations fuse back into one species.
2. Speciation by reinforcement.
3. Two separated populations stay genetically distinct while hybrid swarms form in the zone of contact.
4. Genome recombination results in speciation of the two populations, with an additional hybrid species . All three species are separated by intrinsic reproductive barriers. [ 31 ]