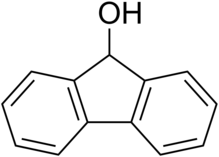
Fluorenol
In the most significant isomer, fluoren-9-ol or 9-hydroxyfluorene, the hydroxy group is located on the bridging carbon between the two benzene rings.
[4] Fluorenol was patented as an insecticide in 1939,[5] and is an algaecide against the green algae Dunaliella bioculata.
[11] There is no evidence (binding assays, occupancy, predicted structure) to suggest that fluorenol acts as a 5-HT6 antagonist, contrary to some popular claims.
[medical citation needed] The unscheduled nature of fluorenol has caused it to fall into a legal grey area in most countries.
Despite being associated with modafinil,[13] fluorenol is not a substituted derivative of it, making its scheduling unimplied by analogue acts.