Foreign relations of China
"[3] An example of a foreign policy decision guided by "sovereignty and territorial integrity" is not engaging in diplomatic relations with any country that recognizes the Republic of China (Taiwan), which the PRC does not recognise as a separate nation.
The dispute over Aksai Chin (formerly a part of the Indian territory of Ladakh) and South Tibet (China) or Arunachal Pradesh (India) is not settled and plagues Sino-Indian relations.
[27] In March 2024, it was revealed that Japan and the European Union are set to engage in discussions regarding cooperation on advanced materials for next-generation chips and batteries, aiming to decrease their dependence on China.
The criticisms focused on the mistreatment of the Uyghur minority, the systematic destruction of democracy in Hong Kong, repeated military threats against Taiwan, unfair trade practices, and lack of transparency regarding the origins of COVID-19.
[40] A 2022 study from Johns Hopkins University's China Africa Research Initiative found that contrary to popular narratives regarding Hambantota port, there were no Chinese debt-to-equity swaps, no asset seizures, and no "hidden debt.
"[53] The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a free trade agreement between the Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Vietnam.
On 25 October 1971, the People's Republic of China took control of the seat with the passing of UN General Assembly Resolution 2758 by a vote of 76 to 35 with 17 abstentions, with support coming from several NATO countries, the Soviet Union, and India, and a notable opponent being the United States.
[63]: 166 List of countries which the People's Republic of China maintains diplomatic relations with: Generally, the political and sociological concept of face has a significant role in Chinese diplomacy.
The establishment of modern Sino-African relations dates back to the late 1950s when China signed the first official bilateral trade agreement with Algeria, Egypt, Guinea, Somalia, Morocco and Sudan.
Due to the low prices of Chinese-made weaponry and military equipment, an increasing number of African countries shifted their source of supply from traditional providers such as Russia to China.
[297] Over the years a number of building projects have been carried out with Chinese government assistance these include: The Garfield Sobers Gymnasium,[298] two adjustments on the Lloyd Erskine Sandiford Centre, a Home Vegetable Growing Experimental Center, embroidery, grass weaving and feather handicraft.
[333]: 40 With China, Middle Eastern countries benefit from a potential investment source and long-term buyer of oil and gas without the political complications that come with dealing with the United States.
[334] The most prominent political issue advocated through CASCF is a Middle East peace process aimed at resolving the Arab-Israeli conflict (including the territorial disputes that Lebanon and Syria each have with Israel).
[347]: 116 Following the invasion of Afghanistan by the United States and the increased involvement of Russia in the region, China's foreign policy makers began to view the Central Asia as both an area for cooperation and competition between major powers.
Hu's critics say that his government was overly aggressive in asserting its new power, overestimated its reach, and raised the ire of the United States and its allies who are close in proximity to China, such as India, and Japan.
[citation needed] Upon resumption of relationship, China and South Korea have been organizing presidential and governmental visits, working together on the Korean Peninsula, assisting with the development of other countries, and cooperating in numerous areas.
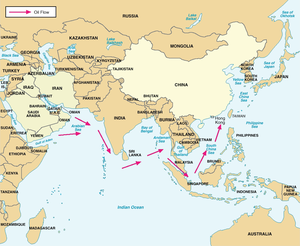
China also lends to and invests in South Asian nations with low-cost financial capital, to help their development sector, especially with the current economically struggling countries of Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Nepal[359]
[372] UK scholar Nasser Amin considers the Sino-Pak entente to be a special kind of relationship in the post-war global system, since there are no natural ties or affinities of culture, religion or ideology that have existed between Islamabad and Beijing; rather, the close relationship appears to substantiate a fundamental premise of the Neo-Realist school of IR thought: namely, that states join in alliance with other states on the basis of power considerations, in this case a shared hostility to India.
[403][404] In September 2022, Li Zhanshu, the third highest-ranking member of the CCP Politburo Standing Committee, told a group of Russian legislators that the Chinese government "understands and supports Russia...on the situation in Ukraine".
[citation needed] In 2003, China announced it intended to enhance its diplomatic ties with the Pacific Islands Forum, and increase the economic aid package it provided to that organisation.
[420][421] The delegation also met Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao, who spoke of increased "economic and trade cooperation"; Xinhua reported that the Pacific Island legislators "expressed appreciation for China's assistance" and "reiterated their countries' adherence to the one-China policy".
[422] In August and September 2010, the People's Liberation Army Navy began an unprecedented "goodwill visit" to its Pacific allies, touring Papua New Guinea, Vanuatu, Tonga, New Zealand and Australia.
[424] In May 2011, addressing the University of the South Pacific in Suva, PRC Ambassador to Fiji Han Zhiqiang stated that Sino-Pacific cooperation had resulted in "plenty of substantial outcomes and benefits for the people in this region".
This multilateral agreement would cover various issues including law enforcement cooperation and training, communications infrastructure, cybersecurity, climate change, healthcare, and a proposed China-Pacific Islands Free Trade Area.
[457] In 2003, Chinese embassy in Port Moresby published a statement of concern in reaction to comments in the Papua New Guinea press questioning the justification for PNG's relations with the People's Republic.
Traditionally, military training aid in Papua New Guinea had been provided by Western countries, namely, Australia, New Zealand and the U.S.[461] The diplomatic relations between China and Samoa were established in 1975.
[464] In March 2008, following unrest in Tibet, the speaker of the Samoan Fono (legislative assembly), Tolofuaivalelei Falemoe Leiataua, stated that foreign leaders should not interfere with China as it deals with "internal affairs", and that they should not meet the Dalai Lama.
Ni-Vanuatu trade minister James Bule said his country had also requested China's assistance "in supplying machines so we can establish a plant in Vanuatu to produce bio fuel".
[479] Jimmy "call[ed] [...] for China to have a foot firmly planted in the Pacific through Port Vila", which -the Vanuatu Daily Post remarked- "no doubt caused ruffled feathers among other foreign diplomatic partners".
[480] In July 2010, Chinese Ambassador Cheng Shuping announced that China would fund a number of projects in Vanuatu, "including the National Convention Centre and the expansion of Prime Minister's Offices", as well as "the design and reconstruction of the Francophone Wing of the University of the South Pacific Emalus Campus".