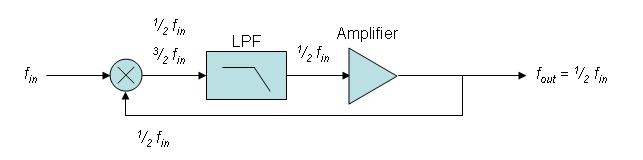
Frequency divider
Digital dividers implemented in modern IC technologies can work up to tens of GHz.
The ILFD locking range is inversely proportional to the quality factor (Q) of the oscillator tank.
In integrated circuit designs, this makes an ILFD sensitive to process variations.
For power-of-2 integer division, a simple binary counter can be used, clocked by the input signal.
Such division is frequency and phase coherent to the source over environmental variations, including temperature.
By adding additional logic gates to the chain of flip-flops, other division ratios can be obtained.
Integrated circuit logic families can provide a single-chip solution for some common division ratios.
Another popular circuit to divide a digital signal by an even integer multiple is a Johnson counter.
This is a type of shift register network that is clocked by the input signal.
(Classification: asynchronous sequential logic) An arrangement of D flip-flops is a classic method for integer-n division.
Such division is frequency and phase coherent to the source over environmental variations, including temperature.
Standard, classic logic chips that implement this or similar frequency division functions include the 7456, 7457, 74292, and 74294.
(see list of 7400 series and list of 4000 series logic chips) A fractional-n frequency synthesizer can be constructed using two integer dividers, a divide-by-N, and a divide-by-(N + 1) frequency divider.
With a modulus controller, N is toggled between the two values so that the VCO alternates between one locked frequency and the other.
Delta-sigma fractional-n dividers overcome this problem by randomizing the selection of N and (N + 1) while maintaining the time-averaged ratios.