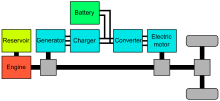
Hybrid vehicle drivetrain
Other combinations offer efficiency gains from superior energy management and regeneration that are offset by cost, complexity and battery limitations.
One of the earliest forms of hybrid land vehicle was the 'trackless' trolleybus experiment in The United States (New Jersey) that ran from 1935 to 1948, which normally used traction current delivered by wire.
The trolleybus was fitted with an internal combustion engine to power the mechanical drivetrain directly, not to generate electricity for the traction motor.
Since the 1990s trolleybus hybrids have been introduced with small power plants to provide a low speed capability for emergency and maintenance but not to support general revenue service.
(An example of this principle is a bicycle fitted with a front hub motor, which assists the cyclist's pedal power at the rear wheel.)
Series hybrids with particular characteristics are classified as range-extended battery-electric vehicle (BEVx) by the California Air Resources Board.
Nissan's e-Power line (Note,[7] Serena,[8] Kicks,[9] X-Trail,[10] and Qashqai)[11] using the engine to drive a generator and the EM57 traction motor.
Supercapacitors combined with a lithium ion battery bank have been used by AFS Trinity in a converted Saturn Vue SUV vehicle.
ICE torque output is minimal at lower RPMs and conventional vehicles increase engine size to meet market requirements for acceptable initial acceleration.
Interesting variations of the simple design (pictured at right) found, for example, in the well-known Toyota Prius are the: The Toyota Hybrid System THS / Hybrid Synergy Drive has a single power-split device (incorporated as a single three-shaft planetary gearset) and can be classified as an Input-Split, since the power of the engine is split at the input to the transmission.
The system was also featured on the GMC Graphite SUV concept vehicle at the 2005 North American International Auto Show in Detroit.
The objective of the design is to vary the percentage of mechanically vs. electrically transmitted power to cope both with low-speed and high-speed operating conditions.
Micro hybrid is a general term given to vehicles that use some type of start-stop system to automatically shut off the engine when idling.
Accessories can continue to run on electrical power while the engine is off, and as in other hybrid designs, regenerative braking recaptures energy.
General Motors then introduced their BAS Hybrid system, another mild-hybrid implementation officially released on the 2007 Saturn Vue Green Line.
However the GM BAS Hybrid System can also provide modest assist under acceleration and during steady driving, and captures energy during regenerative (blended) braking.
It is essentially a large starter motor that operates when the engine needs to be turned over and when the driver "steps on the gas" and requires extra power.
Before 2015, Honda's hybrids, including the Insight, used this design, leveraging their expertise in small, efficient gasoline engines; their system is dubbed Integrated Motor Assist (IMA).
Another variation is the Saturn Vue Green Line BAS Hybrid system that uses a smaller electric motor (mounted to the side of the engine) and battery pack than the Honda IMA, but functions similarly.
To balance the forces from each portion, the vehicles use a differential-style linkage between the engine and motor connected to the head end of the transmission.
Prototypes of PHEVs, with larger battery packs that can be recharged from the power grid, were built in the U.S., notably at Andy Frank's Hybrid Center[47] at University of California, Davis.
With the addition of 140 kg (300 lb) of lead–acid batteries, the PRIUS+ achieved roughly double the gasoline mileage of a standard Prius and could make trips of up to 16 kilometres (10 mi) using only electric power.
[52][53] General Motors began deliveries of the Chevrolet Volt in the United States in December 2010,[5] and its sibling, the Opel Ampera, was released in Europe by early 2012.
That concept is not unique to hybrids; Subaru pioneered this feature in the early 1980s, and the Volkswagen Lupo 3L is one example of a conventional vehicle that shuts off its engine when at a stop.
A British company, Artemis Intelligent Power, made a breakthrough by introducing an electronically controlled hydraulic motor/pump that is efficient at all ranges and loads, making small applications of petro-hydraulic hybrids feasible.
[64] The kinetic braking energy recovery rate is higher and therefore the system is more efficient than 2013-era battery charged hybrids, demonstrating a 60% to 70% increase in economy in EPA testing.
[67][68][69] In January 2011, Chrysler announced a partnership with the EPA to design and develop an experimental gasoline-hydraulic hybrid powertrain suitable for use in passenger cars.
The company claimed a standard pickup vehicle powered by a 2.3-litre, 4-cylinder engine achieved 14 mpg (16.8 L/100 km) in city driving.
The system is similar to that of a hybrid-electric vehicle in that braking energy is harnessed and stored to assist the engine as needed during acceleration.
The aftermarket solution is used when the user delivers glider (rolling chassis) and the hybrid (two engines) or all-electric (only an electric motor) powertrain kit to the automaker and receives the vehicle with the tech installed.