Function model
[7] In the 1960s it was exploited by the NASA to visualize the time sequence of events in a space systems and flight missions.
The main concept in this modeling perspective is the process, this could be a function, transformation, activity, action, task etc.
In general, this process of decomposition is undertaken either for the purpose of gaining insight into the identity of the constituent components, or for the purpose of obtaining a compressed representation of the global function, a task which is feasible only when the constituent processes possess a certain level of modularity.
Functional decomposition has a prominent role in computer programming, where a major goal is to modularize processes to the greatest extent possible.
In the early decades of computer programming, this was manifested as the "art of subroutining," as it was called by some prominent practitioners.
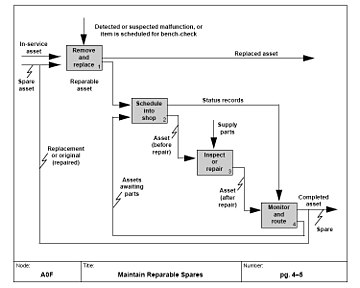
In the system context, the functional flow steps may include combinations of hardware, software, personnel, facilities, and/or procedures.
[18] It was used to develop requirements, construct the design, and support implementation of an expert system to demonstrate automated rendezvous.
[18] The N2 Chart is a diagram in the shape of a matrix, representing functional or physical interfaces between system elements.
The system functions are placed on the diagonal; the remainder of the squares in the N × N matrix represent the interface inputs and outputs.
It offers building blocks to represent entities and activities, and a variety of arrows to relate boxes.
The SADT method allows to define user needs for IT developments, which is used in industrial Information Systems, but also to explain and to present an activity's manufacturing processes, procedures.
These functions fulfill the objectives of a company, such as sales, order planning, product design, part manufacturing, and human resource management.
[25] It was derived from the established graphic modeling language structured analysis and design technique (SADT) developed by Douglas T. Ross and SofTech, Inc.
IDEF0 should assist in organizing system analysis and promote effective communication between the analyst and the customer through simplified graphical devices.
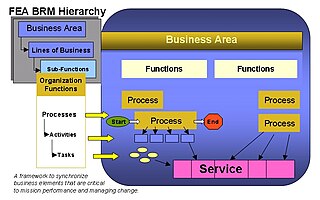
A Business Function Model (BFM) is a general description or category of operations performed routinely to carry out an organization's mission.
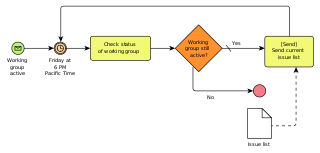
Processes are a group of related business activities performed to produce an end product or to provide a service.
Unlike business functions that are performed on a continual basis, processes are characterized by the fact that they have a specific beginning and an end point marked by the delivery of a desired output.
The BPMN specification also provides a mapping between the graphics of the notation to the underlying constructs of execution languages, particularly BPEL4WS.
These reference model can be constructed in layers, and offer a foundation for the analysis of service components, technology, data, and performance.
The Operator Function Model (OFM) is proposed as an alternative to traditional task analysis techniques used by human factors engineers.
The model represents basic issues of knowledge representation, information flow, and decision making in complex systems.