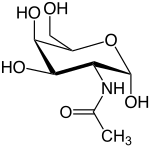
N-Acetylgalactosamine
N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), is an amino sugar derivative of galactose.
In humans it is the terminal carbohydrate forming the antigen of blood group A.
[1] It is typically the first monosaccharide that connects serine or threonine in particular forms of protein O-glycosylation.
N-Acetylgalactosamine is necessary for intercellular communication, and is concentrated in sensory nerve structures of both humans and animals.
GalNAc is also used as a targeting ligand in investigational antisense oligonucleotides and siRNA therapies targeted to the liver, where it binds to the asialoglycoprotein receptors on hepatocytes.