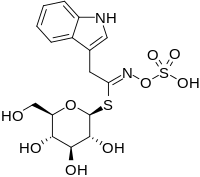
Glucobrassicin
Glucobrassicin is a type of glucosinolate that can be found in almost all cruciferous plants, such as cabbages, broccoli, mustards, and woad.
[4] Tryptophan is converted to indole-3-acetaldoxime (IAOx) by cytochrome p450 enzymes (the redundant CYP92B3 and CYP79B3 in Arabidopsis thaliana) using NADPH and molecular Oxygen.
[5] A separate p450 enzyme (CYP83B1 in Arabidopsis) catalyzes a second subsequent monooxygenase reaction to create a proposed the intermediate 1-aci-nitro-2-indolyl-ethane.
[5] A cysteine is utilized by glutathione S-transferase (GST) in a conjugation process to produce an S-alkylthiohydroximate derivative, which is then cleaved off by a carbon–sulfur lyase (like the SUR1 enzyme found in Arabidopsis) to create a free thiol.
[6] A single glucosylation occurs attaching a glucose molecule to the indole hydroximate through a thioether linkage.