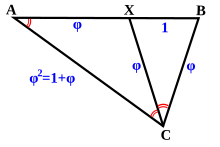
Golden triangle (mathematics)
to the base side: The golden triangle is used to form some points of a logarithmic spiral.
By bisecting one of the base angles, a new point is created that in turn, makes another golden triangle.
[4] The bisection process can be continued indefinitely, creating an infinite number of golden triangles.
[6] Closely related to the golden triangle is the golden gnomon, which is the isosceles triangle in which the ratio of the equal side lengths to the base length is the reciprocal
"The golden triangle has a ratio of base length to side length equal to the golden section φ, whereas the golden gnomon has the ratio of side length to base length equal to the golden section φ.