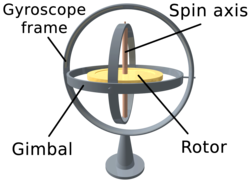
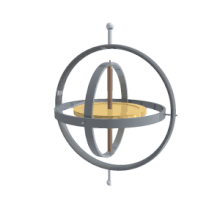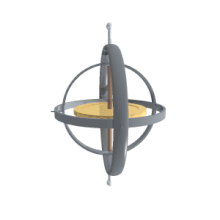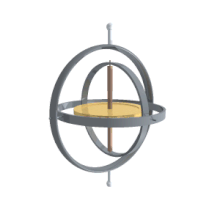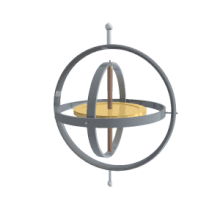
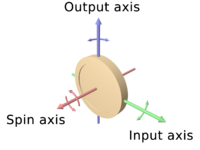
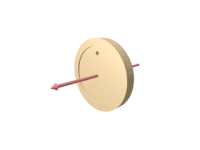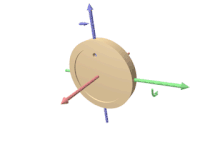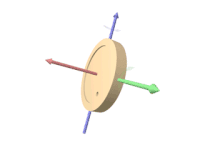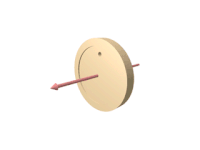
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος gŷros, "round" and σκοπέω skopéō, "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity.
[3] Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine.
[10][11] The French mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace, working at the École Polytechnique in Paris, recommended the machine for use as a teaching aid, and thus it came to the attention of Léon Foucault.
In the 1860s, the advent of electric motors made it possible for a gyroscope to spin indefinitely; this led to the first prototype heading indicators, and a rather more complicated device, the gyrocompass.
[19][20] In the first several decades of the 20th century, other inventors attempted (unsuccessfully) to use gyroscopes as the basis for early black box navigational systems by creating a stable platform from which accurate acceleration measurements could be performed (in order to bypass the need for star sightings to calculate position).
[21][full citation needed] During World War II, the gyroscope became the prime component for aircraft and anti-aircraft gun sights.
Together these sensors provide 6 component motion sensing; accelerometers for X, Y, and Z movement, and gyroscopes for measuring the extent and rate of rotation in space (roll, pitch and yaw).
Some devices[28][29] additionally incorporate a magnetometer to provide absolute angular measurements relative to the Earth's magnetic field.
Rigidity in space describes the principle that a gyroscope remains in the fixed position on the plane in which it is spinning, unaffected by the Earth's rotation.
Steadicam inventor Garrett Brown operated the shot, walking through a redwood forest, running the camera at one frame per second.
When being used in an airplane, for example, it will slowly drift away from north and will need to be reoriented periodically, using a magnetic compass as a reference.
The first gyrostat was designed by Lord Kelvin to illustrate the more complicated state of motion of a spinning body when free to wander about on a horizontal plane, like a top spun on the pavement, or a bicycle on the road.
[42] In modern times, the gyrostat concept is used in the design of attitude control systems for orbiting spacecraft and satellites.
[43] For instance, the Mir space station had three pairs of internally mounted flywheels known as gyrodynes or control moment gyroscopes.
[45] Examples include a solid body with a cavity filled with an inviscid, incompressible, homogeneous liquid,[46] the static equilibrium configuration of a stressed elastic rod in elastica theory,[47] the polarization dynamics of a light pulse propagating through a nonlinear medium,[48] the Lorenz system in chaos theory,[49] and the motion of an ion in a Penning trap mass spectrometer.
Accuracy parameters are increased by using low-intrinsic damping materials, resonator vacuumization, and digital electronics to reduce temperature dependent drift and instability of control signals.
However, the dynamic inertia (from the gyroscopic reaction effect) from the gimbal provides negative spring stiffness proportional to the square of the spin speed (Howe and Savet, 1964; Lawrence, 1998).
This gyroscope took many years to develop, and the experimental models went through many changes before it was deemed ready for production by the engineers and managers of Honeywell and Boeing.
The material of the block was also changed from quartz to a new glass ceramic Cer-Vit, made by Owens Corning, because of helium leaks.
The two-halves of the split beam travel in opposite directions in a coil of fiber optic cable as long as 5 km.
For example, those used in the Gravity Probe B experiment measured changes in gyroscope spin axis orientation to better than 0.5 milliarcseconds (1.4×10−7 degrees, or about 2.4×10−9 radians) over a one-year period.
[61] The GP-B gyro consists of a nearly-perfect spherical rotating mass made of fused quartz, which provides a dielectric support for a thin layer of niobium superconducting material.
Provided the suspension electronics remain powered, the extreme rotational symmetry, lack of friction, and low drag will allow the angular momentum of the rotor to keep it spinning for about 15,000 years.
A precession, or tilt, in the orientation of the rotor causes the London moment magnetic field to shift relative to the housing.
The moving field passes through a superconducting pickup loop fixed to the housing, inducing a small electric current.
Its motion is influenced by the principle of gyroscopic precession which is the concept that a force applied to a spinning object will have a maximum reaction approximately 90 degrees later.
An assembly consisting of a flywheel mounted in a gimbal housing under the hood of the vehicle acted as a large gyroscope.
The integration of the gyroscope has allowed for more accurate recognition of movement within a 3D space than the previous lone accelerometer within a number of smartphones.
Examples of such applications include smartphones such as the Samsung Galaxy Note 4,[68] HTC Titan,[69] Nexus 5, iPhone 5s,[70] Nokia 808 PureView[71] and Sony Xperia, game console peripherals such as the PlayStation 3 controller and the Wii Remote, and virtual reality headsets such as the Oculus Rift.
[74] It is also included in the 3DS, Wii U GamePad, and Nintendo Switch Joy-Con and Pro controllers, which detect movement when turning and shaking.