Heavy-chain antibody
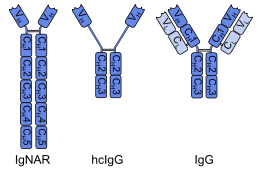
In common antibodies, the antigen binding region consists of the variable domains of the heavy and light chains (VH and VL).
These differences, in combination with the phylogenetic age of the cartilaginous fishes, have led to the hypothesis that IgNAR could be more closely related to a primordial antigen-binding protein than the mammalian immunoglobulins.
To test this hypothesis, it would be necessary to discover IgNAR or similar antibodies in vertebrates that are phylogenetically still older, like the jawless fish lamprey and hagfish.
As well, they are easily isolated using the same phage panning procedure used for traditional antibodies, allowing them to be cultured ex vivo in large concentrations.
[citation needed] Phage-displayed dromedary camel VHH libraries have been made for isolating single-domain antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and other virus infections.