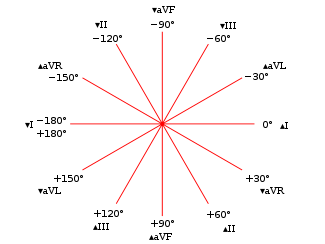
Hexaxial reference system
The hexaxial reference system, better known as the Cabrera system, is a convention to present the extremity leads of the 12 lead electrocardiogram,[1] that provides an illustrative logical sequence that helps interpretation of the ECG, especially to determine the heart's electrical axis in the frontal plane.
The most practical way of using this is by arranging extremity leads according to the Cabrera system, reversing polarity of lead aVR and presenting ECG complexes in the order (aVL, I, -aVR, II, aVF, III).
Example: If lead I has the highest amplitude (higher than aVL or -aVR), the axis is approximately 0°.
[citation needed] An alternative use is to locate the most isoelectric (or equiphasic)[clarification needed] lead (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, or aVF) on a diagnostic quality ECG with proper lead placement.
If lead II is positively deflected on the ECG, the heart's electrical axis in the frontal plane will be approximately +60°.